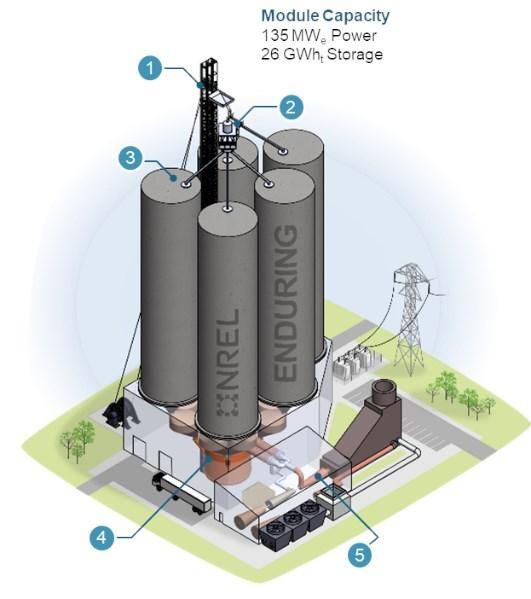
Denver Public Library Powered with Fail-Safe Battery Energy Storage System – Mile High CRE

Report on the Deployment of a Solar and Battery Energy Storage System at the Denver Public Library
Project Overview
- Location: Denver Public Library, City and County of Denver.
- Project: Deployment of the first Solar and Battery Energy Storage System (BESS) for the municipality.
- Partners: Viridi (BESS provider), McKinstry (construction and integration), and the Denver Public Library.
- Technology: Viridi RPSLinkEX fail-safe energy storage solution.
- Objective: To enhance energy resilience, sustainability, and cost savings while adhering to the highest safety standards for public infrastructure.
Alignment with Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs)
-
SDG 7: Affordable and Clean Energy
The project directly advances SDG 7 by promoting access to affordable, reliable, sustainable, and modern energy.
- It increases the share of renewable energy in the library’s energy mix by capturing and utilizing solar power.
- The system reduces peak demand, contributing to grid stability and energy efficiency.
- It ensures a reliable supply of clean backup power during outages.
-
SDG 11: Sustainable Cities and Communities
This initiative makes urban infrastructure more inclusive, safe, resilient, and sustainable.
- It enhances the resilience of a critical public facility, the Denver Public Library, against power disruptions.
- The use of Viridi’s fail-safe technology eliminates fire risks associated with traditional lithium-ion batteries, ensuring the safety of staff and visitors in a public space.
- The project serves as a benchmark for sustainable urban development in Denver.
-
SDG 9: Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure
The deployment showcases the role of innovation in building resilient and sustainable infrastructure.
- It utilizes Viridi’s proprietary fail-safe anti-propagation technology, an innovation in battery safety.
- The project represents a significant upgrade to the city’s public infrastructure, integrating clean technology.
- The system is monitored through the ViSTA Dashboard, demonstrating the integration of modern digital tools in infrastructure management.
-
SDG 17: Partnerships for the Goals
The project’s success is a result of a multi-stakeholder partnership to achieve sustainable development.
- It exemplifies a successful collaboration between a technology provider (Viridi), a national construction leader (McKinstry), and a public entity (Denver Public Library).
- This partnership model is crucial for deploying advanced, sustainable technologies in the public sector.
System Specifications and Functionality
- System Type: Behind-the-meter Viridi RPSLinkEX energy storage solution.
- Primary Functions:
- Stores excess solar energy for use during non-solar hours.
- Reduces energy costs by lowering peak electricity demand.
- Provides dependable backup power during grid outages.
- Key Safety Feature: The system’s fail-safe technology prevents thermal propagation events, making it one of the safest battery solutions for occupied public buildings and meeting Denver’s rigorous fire safety standards.
Conclusion and Future Implications
The Denver Public Library project sets a new standard for how municipalities can integrate renewable energy and battery storage without compromising public safety. By prioritizing fail-safe technology, the City and County of Denver demonstrates a commitment to achieving its sustainability objectives responsibly. This installation serves as a replicable model for other communities seeking to build cleaner, more resilient energy infrastructure in alignment with the Sustainable Development Goals.
Analysis of the Article in Relation to Sustainable Development Goals
1. Which SDGs are addressed or connected to the issues highlighted in the article?
-
SDG 7: Affordable and Clean Energy
- The article focuses on the deployment of a “Solar and Battery Energy Storage System.” This directly addresses the goal of ensuring access to affordable, reliable, sustainable, and modern energy by promoting renewable energy (solar) and clean technology (battery storage).
-
SDG 9: Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure
- The project involves building resilient and sustainable infrastructure. The article highlights the installation of a “fail-safe battery energy storage system” that provides “dependable backup power during outages,” thus enhancing the resilience and sustainability of the Denver Public Library’s infrastructure.
-
SDG 11: Sustainable Cities and Communities
- The project is implemented in an urban public facility, the Denver Public Library, making the city more sustainable and resilient. The article states the project underscores “the city’s commitment to sustainability and energy resilience” and sets a “new benchmark for how cities can combine renewable energy and battery storage.”
-
SDG 17: Partnerships for the Goals
- The successful deployment of the energy system was a result of a partnership between multiple entities. The article explicitly mentions the partnership between “Viridi… McKinstry… and the city and counties of Denver” to achieve a common sustainability goal.
2. What specific targets under those SDGs can be identified based on the article’s content?
-
Targets under SDG 7:
- Target 7.2: By 2030, increase substantially the share of renewable energy in the global energy mix. The article describes the system’s function to “capture excess solar energy for use during non-solar hours,” directly contributing to increasing the share and utilization of renewable energy.
- Target 7.a: By 2030, enhance international cooperation to facilitate access to clean energy research and technology, including renewable energy, energy efficiency and advanced and cleaner fossil-fuel technology, and promote investment in energy infrastructure and clean energy technology. The project itself, being a “first-of-its-kind Solar and Battery Energy Storage System for the city,” represents an investment in and deployment of clean energy technology and infrastructure.
-
Targets under SDG 9:
- Target 9.1: Develop quality, reliable, sustainable and resilient infrastructure… to support economic development and human well-being. The system is described as providing “dependable backup power during outages,” which directly enhances the reliability and resilience of the library’s infrastructure.
- Target 9.4: By 2030, upgrade infrastructure and retrofit industries to make them sustainable, with increased resource-use efficiency and greater adoption of clean and environmentally sound technologies. The installation of the RPSLinkEX system is an upgrade to the library’s existing infrastructure, making it more sustainable through the adoption of “fail-safe battery storage” and solar technology.
-
Targets under SDG 11:
- Target 11.6: By 2030, reduce the adverse per capita environmental impact of cities. By using solar power and reducing peak demand on the grid, the project helps lower the city’s reliance on traditional energy sources, thereby reducing its environmental impact.
- Target 11.b: By 2030, substantially increase the number of cities and human settlements adopting and implementing integrated policies and plans towards… resilience to disasters. The project is a tangible implementation of a plan to increase Denver’s “energy resilience” by ensuring critical public facilities like the library have backup power during outages.
-
Targets under SDG 17:
- Target 17.17: Encourage and promote effective public, public-private and civil society partnerships. The article highlights the project as a successful collaboration between private companies (Viridi and McKinstry) and a public entity (the City and County of Denver), demonstrating an effective public-private partnership.
3. Are there any indicators mentioned or implied in the article that can be used to measure progress towards the identified targets?
-
Indicators for SDG 7 Targets:
- The deployment of a solar and battery storage system is a direct indicator of investment in clean energy technology (relevant to Target 7.a). The system’s capacity to “capture excess solar energy” and “reduce peak demand” can be quantified to measure the increase in renewable energy consumption and energy efficiency (relevant to Target 7.2).
-
Indicators for SDG 9 Targets:
- The successful installation of the “first-of-its-kind” system in Denver serves as an indicator of the adoption of clean and sustainable technologies in infrastructure (relevant to Target 9.4). The system’s feature of providing “dependable backup power during outages” is a direct measure of enhanced infrastructure resilience (relevant to Target 9.1).
-
Indicators for SDG 11 Targets:
- Progress can be measured by the reduction in the library’s grid energy consumption and associated carbon emissions, which contributes to reducing the city’s per capita environmental impact (relevant to Target 11.6). The project itself, as a concrete action to bolster “energy resilience,” serves as an indicator for the implementation of resilience plans (relevant to Target 11.b).
-
Indicators for SDG 17 Targets:
- The existence of the successful partnership between Viridi, McKinstry, and the City of Denver is a qualitative indicator. The financial investment and scope of the project could serve as a quantitative indicator for the value of public-private partnerships in sustainable development (relevant to Target 17.17).
4. Summary Table of SDGs, Targets, and Indicators
| SDGs | Targets | Indicators Identified in the Article |
|---|---|---|
| SDG 7: Affordable and Clean Energy | 7.2: Increase the share of renewable energy. 7.a: Promote investment in clean energy technology. |
Deployment of a solar and battery system; capacity to capture solar energy and reduce peak demand. |
| SDG 9: Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure | 9.1: Develop reliable, sustainable and resilient infrastructure. 9.4: Upgrade infrastructure with clean technologies. |
Provision of “dependable backup power during outages”; installation of a “fail-safe” battery storage system. |
| SDG 11: Sustainable Cities and Communities | 11.6: Reduce the environmental impact of cities. 11.b: Implement plans for resilience. |
Project contributes to the city’s “sustainability” by using renewable energy; tangible implementation of “energy resilience.” |
| SDG 17: Partnerships for the Goals | 17.17: Encourage effective public-private partnerships. | Successful partnership between private companies (Viridi, McKinstry) and a public entity (City of Denver). |
Source: milehighcre.com

What is Your Reaction?
 Like
0
Like
0
 Dislike
0
Dislike
0
 Love
0
Love
0
 Funny
0
Funny
0
 Angry
0
Angry
0
 Sad
0
Sad
0
 Wow
0
Wow
0


















































.jpg.webp?itok=0ZsAnae9#)