Indiana ranks 7th lowest in U.S. for college spending per student – FOX 55 Fort Wayne

Report on U.S. Higher Education Spending and its Alignment with Sustainable Development Goals
Executive Summary
A recent analysis of higher education expenditure in the United States reveals significant disparities among states, with direct implications for the achievement of the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). The study, based on data from the National Center for Education Statistics and the U.S. Bureau of Economic Analysis, found that Indiana ranks seventh-lowest nationally in per-student spending. This report examines these findings through the lens of the SDGs, particularly those concerning quality education and inequality.
Implications for Sustainable Development Goals
The disparities in educational investment directly impact the progress toward several key SDGs:
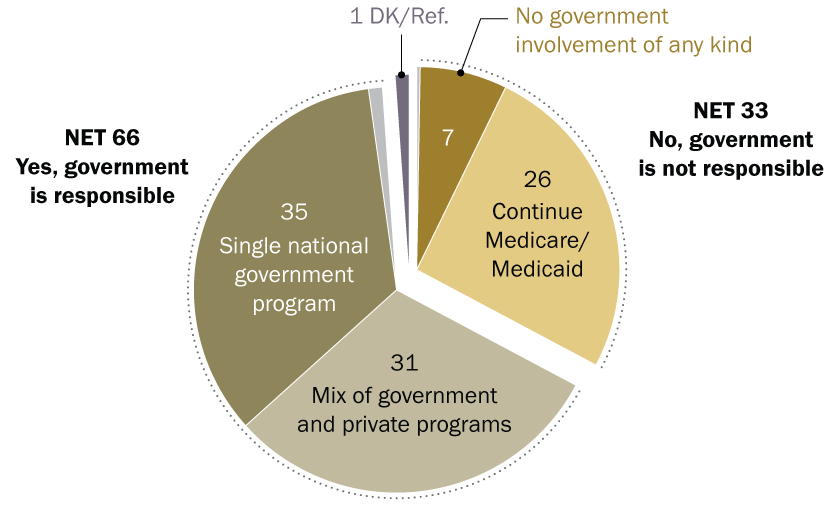
- SDG 4: Quality Education: The core objective of ensuring inclusive and equitable quality education is challenged by the vast differences in funding. Low per-student expenditure, as seen in Indiana ($5,706), can hinder the provision of quality resources, infrastructure, and faculty, thereby affecting the accessibility and quality of tertiary education (Target 4.3).
- SDG 10: Reduced Inequalities: The significant gap in spending between the highest-ranking state (New Jersey: $19,438) and the lowest (Utah: $2,134) highlights intra-country inequality. Such financial disparities in education can perpetuate cycles of economic and social inequality, limiting opportunities for students based on their geographical location.
- SDG 8: Decent Work and Economic Growth: Investment in higher education is fundamental to developing a skilled workforce and fostering innovation, which are critical for sustainable economic growth. Underfunding education can compromise a state’s ability to prepare its citizens for productive employment and decent work.
Key Findings from the Analysis
The research calculated annual expenditure per student by analyzing total state spending on higher education relative to the total number of enrolled students.
State-Level Expenditure Rankings
The analysis identified a wide variance in per-student investment across the nation. Key data points include:
- Highest Spending State: New Jersey leads the nation with an annual expenditure of $19,438 per student.
- Lowest Spending State: Utah has the lowest expenditure, at $2,134 per student.
- Indiana’s Position: With an annual expenditure of $5,706 per student, based on a total budget of nearly $3.5 billion for 607,483 students, Indiana is ranked as the seventh-lowest in the U.S.
Conclusion
The findings underscore a critical need for states to re-evaluate higher education funding to align with the principles of the Sustainable Development Goals. Addressing the significant disparities in per-student spending is essential to ensure that all students have equitable access to quality higher education, which is a foundational element for reducing inequality and promoting long-term sustainable development.
SDGs Addressed or Connected to the Issues Highlighted
SDG 4: Quality Education
- The article directly addresses the theme of quality education by focusing on the financial investment in higher education. It discusses “higher education spending per student,” which is a critical component of ensuring the quality and accessibility of tertiary education. The analysis of Indiana’s $5,706 annual expenditure per student, compared to other states, highlights concerns about the resources available to provide quality university-level education.
SDG 10: Reduced Inequalities
- The article’s core finding is the “disparities in educational spending across states.” By comparing the highest spending state (New Jersey at $19,438 per student) with the lowest (Utah at $2,134), the article underscores significant inequality in educational opportunities based on geographic location within the U.S. This disparity can lead to unequal outcomes for students, which is a central concern of SDG 10.
Specific Targets Identified
Targets under SDG 4: Quality Education
- Target 4.3: By 2030, ensure equal access for all women and men to affordable and quality technical, vocational and tertiary education, including university. The article’s discussion on the “accessibility of college” and the “cost of universities” directly relates to this target. The wide variation in spending per student implies that access to quality and affordable tertiary education is not equal across the states.
Targets under SDG 10: Reduced Inequalities
- Target 10.3: Ensure equal opportunity and reduce inequalities of outcome, including by eliminating discriminatory laws, policies and practices and promoting appropriate legislation, policies and action in this regard. The significant difference in “annual expenditure per student” between states points to an inequality of opportunity. Students in states with lower investment, like Indiana, may not have the same educational resources and opportunities as students in higher-spending states, which can lead to inequalities of outcome in their future careers and economic well-being.
Indicators Mentioned or Implied
Indicators for Target 4.3
- The article provides direct data that can serve as an indicator for measuring the financial commitment to quality tertiary education. The primary indicator is the “Annual expenditure per student ($)”. This metric, calculated for each state, measures the financial resources allocated per student, which is a proxy for the quality and affordability of the education provided.
- Another implied indicator is the “Population enrolled in higher education.” The article provides this data for several states (e.g., Indiana has 607,483 enrolled students). This figure is essential for calculating participation rates in tertiary education, a key aspect of monitoring access.
Indicators for Target 10.3
- The disparity in the “Annual expenditure per student ($)” across different states serves as a direct indicator of inequality in public investment in education. The range presented in the article, from $19,438 in New Jersey to $2,134 in Utah, quantifies the level of inequality in educational opportunity based on geography. Progress towards this target could be measured by a reduction in the variance of this indicator across all states.
SDGs, Targets, and Indicators Table
| SDGs | Targets | Indicators |
|---|---|---|
| SDG 4: Quality Education | Target 4.3: Ensure equal access for all to affordable and quality tertiary education. |
|
| SDG 10: Reduced Inequalities | Target 10.3: Ensure equal opportunity and reduce inequalities of outcome. |
|
Source: wfft.com
What is Your Reaction?
 Like
0
Like
0
 Dislike
0
Dislike
0
 Love
0
Love
0
 Funny
0
Funny
0
 Angry
0
Angry
0
 Sad
0
Sad
0
 Wow
0
Wow
0


















































.jpg.webp?itok=0ZsAnae9#)