Scaling Privacy Infrastructure for GenAI Product Innovation – Engineering at Meta
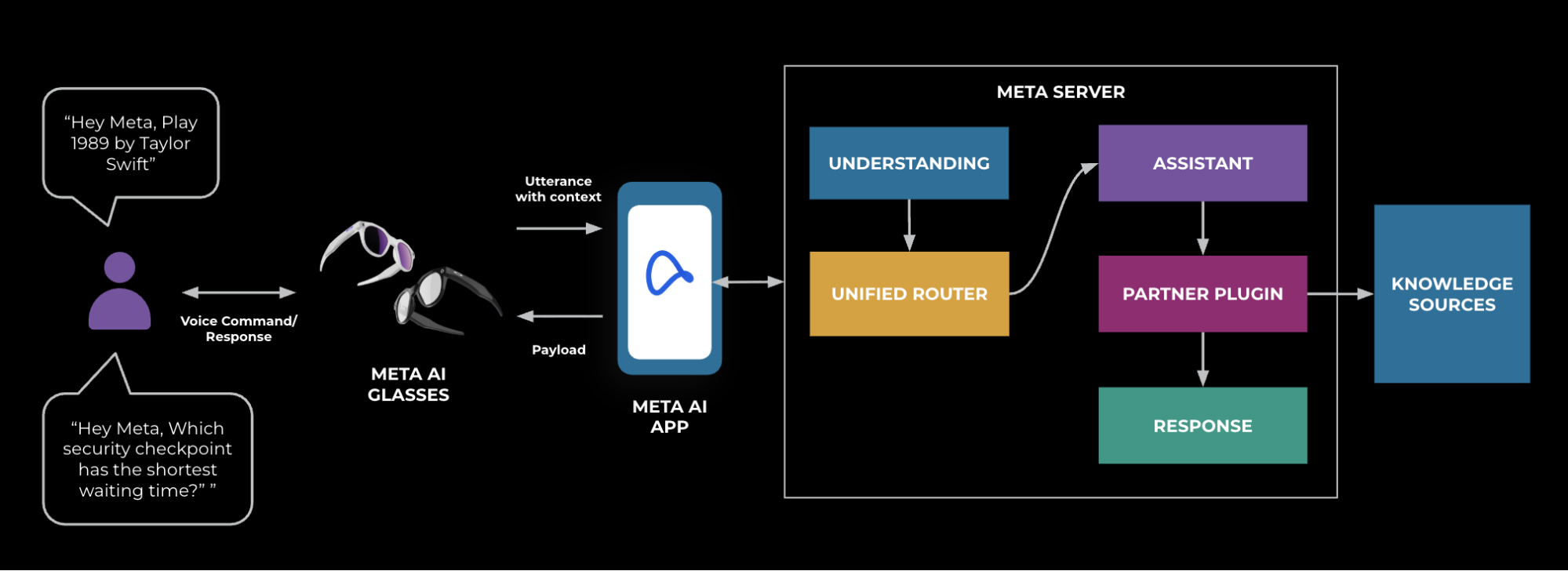
Report on Meta’s Privacy-Aware Infrastructure for Generative AI and Alignment with Sustainable Development Goals
This report analyzes Meta’s strategy for managing data privacy in Generative AI (GenAI) applications. It examines the firm’s Privacy Aware Infrastructure (PAI) as a foundational component for responsible innovation, with a specific focus on its contribution to achieving key United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), particularly SDG 9 (Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure) and SDG 16 (Peace, Justice, and Strong Institutions).
GenAI Innovation and the Imperative for Sustainable Infrastructure
The proliferation of GenAI technologies, such as those powering Meta’s AI glasses, introduces new product capabilities while simultaneously heightening the need for robust data protection frameworks. This dynamic underscores the importance of building resilient and responsible digital infrastructure, a core tenet of SDG 9.
Key Privacy Challenges in the GenAI Era
The integration of GenAI presents three primary challenges to data privacy and sustainable development:
- Technological Evolution and Data Growth: GenAI introduces novel data types and significantly increases data volumes, complicating data observability and management.
- Evolving Regulatory and Compliance Landscape: Continuous technological advancements create new privacy requirements, demanding adaptable infrastructure to maintain compliance and foster innovation.
- Accelerated Innovation Cycles: The rapid development of GenAI-powered features necessitates infrastructure that can scale quickly while automatically enforcing privacy controls.
Alignment with SDG 9: Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure
Meta’s development of a scalable Privacy Aware Infrastructure (PAI) directly addresses these challenges, contributing to SDG 9. By building a resilient infrastructure that embeds privacy from the ground up, the company fosters an environment for sustainable technological innovation. This approach ensures that advancements in AI are not only powerful but also safe, reliable, and aligned with global standards for responsible development.
Meta’s Privacy-Aware Infrastructure (PAI): A Framework for Responsible Governance
Meta’s PAI is a comprehensive suite of services, APIs, and monitoring systems designed to integrate privacy into the product development lifecycle. This system serves as a critical tool for corporate governance and accountability.
Core Components of PAI
The infrastructure is built on three pillars that support responsible data handling:
- Enhanced Observability: Automated data detection and data-lineage tracking provide a real-time map of data origins, propagation, and usage across all systems.
- Efficient Privacy Controls: Policy-enforcement APIs and automated workflows programmatically enforce regional and global privacy constraints at the data storage, processing, and access layers.
- Scalability: The infrastructure is designed to support thousands of microservices and product teams, ensuring consistent privacy application across Meta’s ecosystem.
Supporting SDG 16: Peace, Justice, and Strong Institutions
The PAI framework strengthens institutional accountability and protects fundamental freedoms, aligning with the principles of SDG 16. By creating transparent and verifiable systems for data management, PAI helps build user trust and demonstrates a commitment to upholding the fundamental right to privacy. The automated enforcement of policies ensures that data protection is not an afterthought but an integral, auditable component of the technological architecture, contributing to the development of effective and accountable institutions.
Technical Analysis: Data Lineage as a Tool for Transparency and Accountability
A core technology within the PAI’s “Discover” stage is its data lineage system, which provides the granular visibility necessary to enforce privacy policies and demonstrate compliance, thereby reinforcing the objectives of both SDG 9 and SDG 16.
Cross-Stack Lineage for Complete Data Flow Mapping
To ensure comprehensive traceability of user interaction data, such as from AI glasses, the system maps data movement across the entire technology stack:
- Web Ingestion: Data flows are captured as they enter web servers and move between components.
- Data Persistence: Lineage tracks data from web processing through loggers to data-warehouse tables.
- Inference and Model Interaction: Lineage signals are collected at service boundaries for Large Language Model (LLM) calls, tracking inputs, model checkpoints, and responses.
- Model Training: The system links warehouse tables to training jobs, creating a critical boundary for enforcing purpose limitations on data usage.
Building Comprehensive Lineage Observability
To achieve a complete and accurate map of data flows, the system relies on several key mechanisms:
- Linking Read/Write Operations: All data read operations are linked to corresponding write operations using a consistent correlation key.
- Common Privacy Library (PrivacyLib): A standardized library is used to initialize and propagate privacy policies and log data flow information across diverse systems.
- System-Wide Integration: The library is integrated into all relevant data systems across multiple programming languages to ensure comprehensive coverage of I/O operations.
From Lineage to Verifiable Protection
Data lineage provides the foundation for transforming visibility into tangible data protection and accountability:
- Lineage insights guide the placement of “Policy Zones” to protect sensitive data.
- Automated checks ensure that data assets are only used for permitted purposes, such as model training, blocking non-compliant operations.
- Continuous verification systems monitor data flows over time, identifying and flagging any new or altered data processing jobs for review.
Conclusion: Scaling Responsible AI for Sustainable Global Impact
Meta’s investment in its Privacy Aware Infrastructure demonstrates a scalable model for integrating privacy and accountability into the core of GenAI development. This approach is essential for fostering innovation that is not only technologically advanced but also ethically sound and aligned with global sustainable development priorities.
Key Findings
- The rapid advancement of GenAI necessitates the parallel development of sophisticated, privacy-aware infrastructure to meet new policy challenges, directly supporting SDG 9.
- A structured workflow (Understand -> Discover -> Enforce -> Demonstrate) allows privacy enforcement to scale alongside GenAI product development.
- Scalable data lineage technology is critical for providing the auditable, real-time insight required for effective privacy controls and accountability, a key component of SDG 16.
- Automated guardrails and immediate feedback mechanisms empower product teams to innovate rapidly and safely, reducing friction while upholding foundational principles of trust and privacy.
Future Outlook and Commitment to SDGs
As GenAI continues to evolve, so too will the complexities of privacy protection. The ongoing development of PAI reflects a commitment to advancing infrastructure that enables, rather than hinders, responsible innovation. By scaling privacy infrastructure as a core component of product development, Meta is establishing a foundation for an era of digital experiences that supports sustainable economic growth (SDG 8), fosters resilient innovation (SDG 9), and upholds principles of justice and institutional integrity (SDG 16).
1. Which SDGs are addressed or connected to the issues highlighted in the article?
The article discusses Meta’s development of a Privacy Aware Infrastructure (PAI) to manage Generative AI responsibly. This connects to several Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) centered around innovation, infrastructure, economic growth, and the protection of fundamental freedoms in the digital age.
-
SDG 9: Industry, Innovation and Infrastructure
This goal is central to the article. The text is entirely focused on building a resilient, scalable, and sophisticated digital infrastructure (the PAI) to support and manage technological innovation (GenAI). The article states, “We scale our Privacy Aware Infrastructure (PAI) as a foundational backbone of AI innovation,” directly linking the development of infrastructure to enabling technological progress.
-
SDG 8: Decent Work and Economic Growth
The article highlights how GenAI drives economic activity through rapid product development. It mentions that “GenAI-powered features drive faster product development, necessitating infrastructure that can scale rapidly.” By creating tools like PAI that “accelerate GenAI product innovation,” Meta is contributing to technological upgrading and productivity, which are key drivers of economic growth as outlined in this SDG.
-
SDG 16: Peace, Justice and Strong Institutions
This goal includes protecting fundamental freedoms. The article’s core theme is safeguarding user data privacy, which is a fundamental right in the digital era. Meta’s effort to earn and maintain user trust by “upholding user trust and privacy as foundational principles” and creating systems for “transparent and verifiable privacy guarantees” aligns with the principles of building accountable and transparent institutions (in this case, a corporate entity acting responsibly).
2. What specific targets under those SDGs can be identified based on the article’s content?
Based on the article’s focus on infrastructure, innovation, and privacy, the following specific SDG targets can be identified:
-
Under SDG 9: Industry, Innovation and Infrastructure
- Target 9.1: “Develop quality, reliable, sustainable and resilient infrastructure…to support economic development and human well-being.” The article describes the PAI as a “suite of infrastructure services, APIs, and monitoring systems” designed to be scalable and robust, which directly corresponds to the development of reliable and resilient digital infrastructure.
- Target 9.5: “Enhance scientific research, upgrade the technological capabilities of industrial sectors…encouraging innovation.” The entire initiative is an example of a company upgrading its technological capabilities to manage and encourage innovation in GenAI. The article notes that PAI “empowers engineers to innovate while automatically ensuring policy adherence and safety.”
-
Under SDG 8: Decent Work and Economic Growth
- Target 8.2: “Achieve higher levels of economic productivity through diversification, technological upgrading and innovation.” The article discusses how PAI addresses the challenge of “Accelerated innovation cycles” and helps “product teams move faster and safer,” which directly contributes to achieving higher productivity through technological innovation.
-
Under SDG 16: Peace, Justice and Strong Institutions
- Target 16.10: “Ensure public access to information and protect fundamental freedoms, in accordance with national legislation and international agreements.” The article’s focus on protecting user data and privacy is a direct effort to protect a fundamental freedom. The development of “automated privacy controls” and “policy-enforcement APIs” are mechanisms designed to uphold this right, thereby reinforcing the principles of this target.
3. Are there any indicators mentioned or implied in the article that can be used to measure progress towards the identified targets?
The article does not mention official SDG indicators, but it implies several metrics and systems that can be used to measure progress towards the identified targets:
-
Indicators for SDG 9 (Targets 9.1 & 9.5)
- Implementation of a Scalable Privacy Infrastructure: The existence and functionality of the Privacy Aware Infrastructure (PAI) itself is a primary indicator. The article mentions it “supports thousands of microservices and product teams across Meta’s vast ecosystem.”
- Comprehensive Data Observability: The use of “automated data detection through advanced scanning and tagging” and “data-lineage tracking” provides a measure of the infrastructure’s capability to manage complex data flows.
- Support for Innovation Cycles: The ability of the infrastructure to support “accelerated innovation cycles” for GenAI products serves as an indicator of its effectiveness in fostering innovation.
-
Indicators for SDG 8 (Target 8.2)
- Speed of Product Development: The article implies that a measure of success is enabling product teams to “move faster and safer, with lower friction,” which can be seen as an indicator of increased productivity.
- Launch of New GenAI Products: The successful global rollout of products like the “AI glasses” is presented as a tangible outcome of this innovative infrastructure.
-
Indicators for SDG 16 (Target 16.10)
- Automated Policy Enforcement: The implementation and use of “Policy Zones” and “policy-enforcement APIs” to “programmatically enforce privacy constraints” is a clear indicator of the protection of user data.
- Auditable Data Lineage: The ability to create an “end-to-end graph for interaction data” provides “auditable, real-time insight into every data flow,” serving as a verifiable measure of transparency and policy adherence.
- Continuous Verification and Compliance: The system of “verifiers” that “watch these edges over time” to identify new or changed data-processing jobs is an indicator of ongoing commitment to protecting fundamental freedoms.
4. SDGs, Targets, and Indicators Table
| SDGs | Targets | Indicators (Implied from the article) |
|---|---|---|
| SDG 9: Industry, Innovation and Infrastructure |
|
|
| SDG 8: Decent Work and Economic Growth |
|
|
| SDG 16: Peace, Justice and Strong Institutions |
|
|
Source: engineering.fb.com
What is Your Reaction?
 Like
0
Like
0
 Dislike
0
Dislike
0
 Love
0
Love
0
 Funny
0
Funny
0
 Angry
0
Angry
0
 Sad
0
Sad
0
 Wow
0
Wow
0
















































































