Food Waste Management Market Poised for Robust 6.1% CAGR Growth Through 2035 – openPR.com
Report on the Global Food Waste Management Market and its Contribution to Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs)
Executive Summary
The global Food Waste Management Market is experiencing significant growth, driven by an increasing global focus on sustainability, the circular economy, and the achievement of the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). The market is projected to expand from a valuation of USD 39.5 billion in 2025 to USD 75.9 billion by 2035, reflecting a Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 6.1%. This expansion is directly linked to efforts to address climate change (SDG 13), promote responsible consumption and production (SDG 12), and develop sustainable cities and communities (SDG 11). The transformation of food waste into valuable resources such as biogas, compost, and animal feed is central to this market’s alignment with global sustainability targets.
The Global Imperative for Food Waste Management
The management of food waste is a critical global challenge with profound implications for several SDGs. Annually, over 1.3 billion tons of food, nearly one-third of all food produced for human consumption, is wasted. This issue extends beyond economic loss and directly impacts key sustainability targets:
- SDG 12 (Responsible Consumption and Production): The sheer volume of waste undermines sustainable production patterns. SDG Target 12.3 specifically calls for halving per capita global food waste at the retail and consumer levels by 2030.
- SDG 13 (Climate Action): Food waste decomposing in landfills is a major source of methane, a potent greenhouse gas, directly hindering efforts to combat climate change.
- SDG 2 (Zero Hunger): Reducing food loss and waste is essential to improving food security and ensuring access to nutritious food for all.
In response, governments worldwide are implementing stringent regulations for waste segregation and recycling, creating sustained demand for advanced management solutions.
Market Drivers Aligned with SDG Achievement
Corporate ESG Commitments and SDG 12
Corporate Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) frameworks are compelling food processors, retailers, and hospitality groups to adopt responsible waste management practices. This trend supports SDG 12 by integrating sustainability into corporate strategy. For example, Waste Management Inc.’s expansion of its EcoCycle Commercial Organics platform demonstrates a corporate commitment to waste diversion and transparent reporting.
Technological Advancements for Resource Efficiency
Digitalization is enhancing the market’s capacity to meet SDG targets. AI and IoT-based systems enable precise monitoring and reduction of food waste, contributing to operational efficiency and resource conservation. Solutions from providers like Winnow and LeanPath have demonstrated the potential to reduce food waste in commercial kitchens by 30-50%, directly advancing SDG 12.
Circular Economy Adoption
The shift towards a circular economy is a primary driver, turning waste streams into valuable resources. This model is fundamental to achieving SDG 12. Key circular practices include:
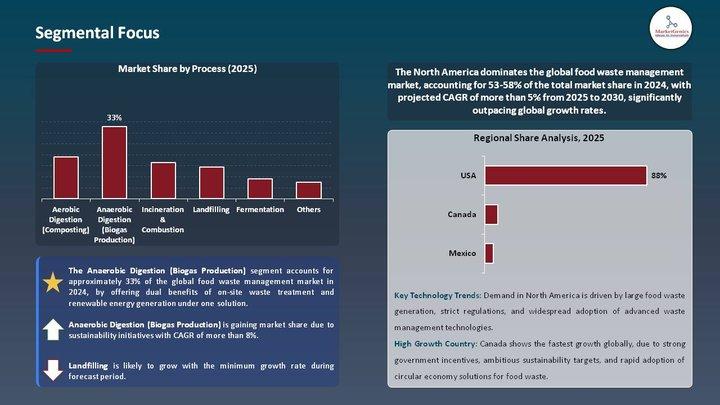
- Anaerobic Digestion: This process, holding a 33% market share, converts organic waste into biogas, contributing to SDG 7 (Affordable and Clean Energy).
- Composting: Creates organic fertilizer, supporting SDG 15 (Life on Land) by improving soil health.
- Fermentation and Animal Feed Production: Provides alternative pathways to valorize food waste.
Emerging Opportunities for SDG Acceleration
Bioenergy and Biogas Production (SDG 7 & SDG 13)
The conversion of food waste to biogas is a rapidly growing segment. This waste-to-energy pathway provides a renewable energy source, reducing reliance on fossil fuels and mitigating greenhouse gas emissions from landfills, thereby supporting both SDG 7 and SDG 13.
Organic Fertilizer and Compost Manufacturing (SDG 2 & SDG 15)
The rising demand for organic fertilizers aligns with the global shift towards sustainable agriculture (SDG 2). Compost derived from food waste offers an eco-friendly alternative to synthetic fertilizers, enhancing soil health and contributing to the protection of terrestrial ecosystems (SDG 15).
Smart Waste Monitoring Solutions (SDG 11 & SDG 12)
Intelligent systems, including AI-powered analytics and smart bins, are creating new opportunities for waste reduction. These technologies help create more sustainable cities (SDG 11) and enable businesses to optimize procurement and minimize waste, fostering responsible consumption patterns (SDG 12).
Food Redistribution Platforms (SDG 2 & SDG 12)
Digital platforms connecting surplus food with non-profits and community kitchens are gaining traction. These initiatives directly address SDG 2 (Zero Hunger) while simultaneously reducing food waste in line with SDG 12.3.
Market Segmentation and Regional Outlook
Segmental Analysis
- By Process: Anaerobic digestion dominates due to its dual benefits of producing renewable energy (SDG 7) and nutrient-rich fertilizer (SDG 15).
- By Source: The commercial sector, including hotels and food processing units, is a primary generator of waste, driving demand for solutions that support corporate sustainability goals under SDG 12.
- By End Use: The production of renewable energy and fertilizers are the fastest-growing end-use segments, reflecting a global policy shift towards climate action (SDG 13) and sustainable agriculture (SDG 2).
Regional Analysis
North America leads the market, supported by stringent regulations and strong corporate adoption of sustainability practices aligned with the SDGs. Europe follows closely, driven by its early adoption of circular economy policies. The Asia Pacific region is experiencing rapid growth, fueled by urbanization and increasing environmental awareness, presenting significant opportunities for implementing waste management solutions that support SDG 11 and SDG 12.
Future Outlook (2025-2035)
The Food Waste Management Market is poised for continued strong growth, with a forecast opportunity of USD 36.4 billion by 2035. The market’s future will be shaped by the integration of circular bioeconomy models, waste-to-resource technologies, and AI-enabled systems. Continued investment in these areas will be critical for companies to maintain a competitive edge and for the global community to advance its progress toward achieving the Sustainable Development Goals, particularly SDG 12, by the 2030 deadline and beyond.
SDGs Addressed in the Article
SDG 2: Zero Hunger
- The article connects food waste management to hunger by mentioning “Food redistribution and donation platforms.” It highlights that these platforms “connect surplus food to NGOs, community kitchens, and shelters,” which directly aligns with the goal of reducing hunger by making use of otherwise wasted food.
SDG 7: Affordable and Clean Energy
- The article discusses converting food waste into energy. It specifically points to “biogas production through anaerobic digestion” as a method for “renewable energy generation, reducing reliance on fossil fuels.” This directly addresses the goal of increasing the share of renewable energy.
SDG 9: Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure
- The article emphasizes the role of technology and infrastructure in managing food waste. It mentions “advanced treatment facilities such as anaerobic digesters and industrial composters” and the integration of “AI-powered waste monitoring, IoT-based tracking systems.” This highlights the development of sustainable infrastructure and the adoption of clean technologies in the waste management industry.
SDG 11: Sustainable Cities and Communities
- The article points to municipal-level actions in waste management. It notes that cities like “New Haven and Washington, D.C. have implemented comprehensive composting programs and smart-bin technology,” which is a direct effort to improve municipal waste management and reduce the environmental impact of cities.
SDG 12: Responsible Consumption and Production
- This is the central SDG addressed. The entire article focuses on managing the “1.3 billion tons of food… wasted every year globally.” It discusses reducing waste generation through prevention, recycling (composting, anaerobic digestion), and reuse (animal feed, redistribution), which are core principles of sustainable consumption and production patterns.
SDG 13: Climate Action
- The article explicitly links food waste to climate change, stating it is a “major source of greenhouse gas emissions, particularly methane from landfills.” The drive for food waste management is framed as a response to “increasing awareness of climate change,” and solutions like biogas production are noted for “minimizing landfill emissions.”
Specific SDG Targets Identified
Targets under SDG 12: Responsible Consumption and Production
- Target 12.3: By 2030, halve per capita global food waste at the retail and consumer levels and reduce food losses along production and supply chains, including post-harvest losses. The article’s core subject is the management and reduction of the “1.3 billion tons of food” wasted annually, which directly addresses this target.
- Target 12.5: By 2030, substantially reduce waste generation through prevention, reduction, recycling and reuse. The article details methods like “composting, and recycling practices,” and turning waste into “biogas, compost, and animal feed,” which are all components of this target.
Targets under SDG 2: Zero Hunger
- Target 2.1: By 2030, end hunger and ensure access by all people… to safe, nutritious and sufficient food all year round. The mention of “Food redistribution and donation platforms that connect surplus food to NGOs, community kitchens, and shelters” is a strategy that contributes to this target by redirecting edible food to those in need.
Targets under SDG 7: Affordable and Clean Energy
- Target 7.2: By 2030, increase substantially the share of renewable energy in the global energy mix. The article identifies “biogas production through anaerobic digestion” as a key market segment for “renewable energy generation,” directly contributing to this target.
Targets under SDG 9: Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure
- Target 9.4: By 2030, upgrade infrastructure and retrofit industries to make them sustainable… and greater adoption of clean and environmentally sound technologies and processes. The article’s focus on “advanced treatment facilities,” “AI and IoT systems,” and “efficient anaerobic digestion” reflects the push for upgrading infrastructure with sustainable and clean technologies.
Targets under SDG 11: Sustainable Cities and Communities
- Target 11.6: By 2030, reduce the adverse per capita environmental impact of cities, including by paying special attention to… municipal and other waste management. The article provides examples of cities implementing “comprehensive composting programs and smart-bin technology,” which are direct actions to improve municipal waste management as specified in this target.
Targets under SDG 13: Climate Action
- Target 13.2: Integrate climate change measures into national policies, strategies and planning. The article notes that “Governments worldwide are tightening regulations to mandate proper food waste segregation, composting, and recycling practices” partly due to the awareness that food waste is a “major source of greenhouse gas emissions.” This shows the integration of waste management as a climate action strategy.
Indicators for Measuring Progress
Indicators for Target 12.3 (Halve food waste)
- Quantitative measure of food waste: The article provides a baseline figure: “More than 1.3 billion tons of food are wasted every year globally,” which is a direct indicator of the scale of the problem (related to SDG Indicator 12.3.1).
- Percentage reduction in waste: The article mentions that AI-based tools can “reduce waste by up to 30-50% within commercial kitchens,” providing a measurable indicator of progress in waste prevention.
Indicators for Target 12.5 (Reduce waste generation)
- Market share of recycling technologies: The article states that the “anaerobic digestion segment capturing ~33% market share” serves as an indicator of the adoption rate of a key recycling and waste-to-resource technology.
Indicators for Target 7.2 (Increase renewable energy share)
- Growth of waste-to-energy sector: The article describes “biogas production through anaerobic digestion” as one of the “fastest-growing segments” and notes that “Waste-to-energy solutions are expanding rapidly.” The growth rate and market size (projected to reach USD 75.9 billion by 2035) can be used as indicators.
Indicators for Target 9.4 (Upgrade to sustainable infrastructure)
- Market growth and investment: The projected growth of the Food Waste Management Market from “USD 39.5 billion in 2025” to “USD 75.9 billion by 2035” indicates the level of investment in sustainable waste management infrastructure and technology.
- Adoption of advanced technologies: The implementation of “AI-powered waste analytics tools, smart bins, and computer vision systems” by hospitality chains and supermarkets is a qualitative and quantifiable indicator of technological adoption.
Indicators for Target 11.6 (Improve municipal waste management)
- Implementation of municipal programs: The article explicitly mentions the implementation of “comprehensive composting programs and smart-bin technology” in cities like New Haven and Washington, D.C., which serves as a direct indicator of improved city-level waste management.
Summary Table of SDGs, Targets, and Indicators
| SDGs | Targets | Indicators Identified in the Article |
|---|---|---|
| SDG 12: Responsible Consumption and Production | 12.3: Halve per capita global food waste. 12.5: Substantially reduce waste generation through prevention, reduction, recycling and reuse. |
– Total global food waste: “1.3 billion tons of food are wasted every year.” – Percentage reduction achieved by technology: “reduce waste by up to 30-50% within commercial kitchens.” – Market share of recycling methods: “anaerobic digestion segment capturing ~33% market share.” |
| SDG 2: Zero Hunger | 2.1: End hunger and ensure access to safe, nutritious and sufficient food. | – Existence and traction of “Food redistribution and donation platforms” connecting surplus food to NGOs and community kitchens. |
| SDG 7: Affordable and Clean Energy | 7.2: Increase substantially the share of renewable energy in the global energy mix. | – Growth of the biogas segment: “One of the fastest-growing segments… is biogas production.” – Adoption of waste-to-energy solutions for “renewable energy generation.” |
| SDG 13: Climate Action | 13.2: Integrate climate change measures into policies and planning. | – Reduction of greenhouse gas emissions: Managing food waste to minimize “methane from landfills.” – Implementation of government regulations on waste segregation as a climate response. |
| SDG 9: Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure | 9.4: Upgrade infrastructure and retrofit industries to make them sustainable. | – Market growth as a proxy for investment: Market value expected to reach “USD 75.9 billion by 2035.” – Adoption of advanced systems: “AI-powered waste monitoring, IoT-based tracking systems.” |
| SDG 11: Sustainable Cities and Communities | 11.6: Reduce the adverse per capita environmental impact of cities, including waste management. | – Implementation of city-level programs: “comprehensive composting programs and smart-bin technology” in cities like New Haven and Washington, D.C. |
Source: openpr.com
What is Your Reaction?
 Like
0
Like
0
 Dislike
0
Dislike
0
 Love
0
Love
0
 Funny
0
Funny
0
 Angry
0
Angry
0
 Sad
0
Sad
0
 Wow
0
Wow
0













































































