Green Cloud Computing for Enterprises: Sustainability Guide – appinventiv.com
Report on Green Cloud Computing and its Alignment with Sustainable Development Goals
Introduction: The ESG Imperative and Global Goals
Enterprises face increasing pressure to align business growth with global sustainability targets. Green cloud computing presents a strategic pathway for organizations to reduce their environmental impact while enhancing operational efficiency. This report details the role of sustainable cloud solutions in achieving Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) objectives, with a significant emphasis on their contribution to the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs).
Market Trends and Analysis: The Shift Towards Sustainable Infrastructure
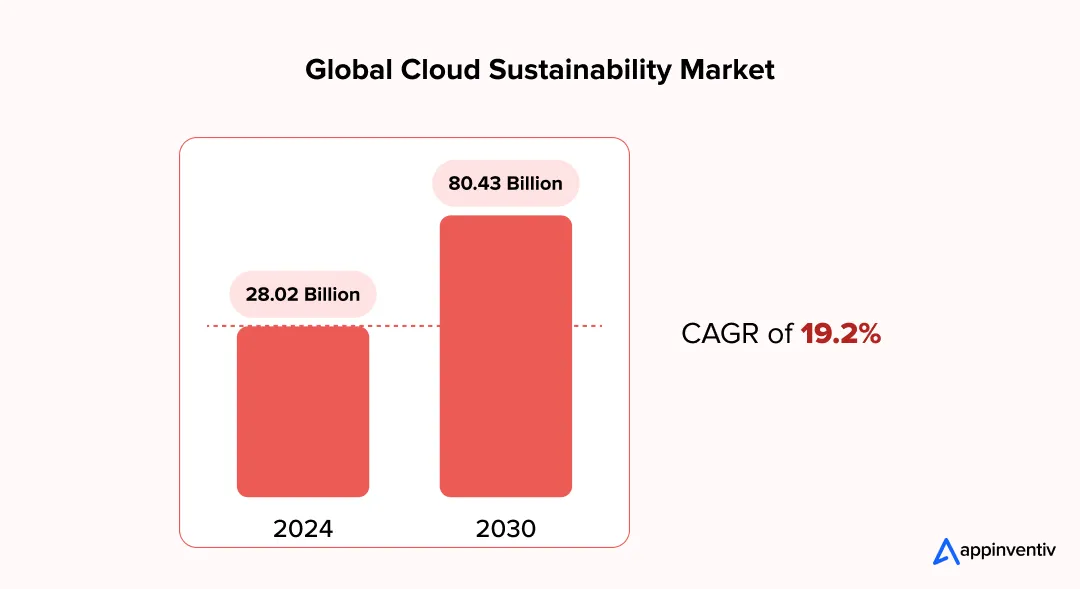
Global Market Growth
The global green data center market is projected to expand from $28.02 billion in 2024 to $80.43 billion by 2030, at a CAGR of 19.2%. This growth signifies a substantial capital pivot towards infrastructure that supports SDG 9 (Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure) and SDG 13 (Climate Action).
Primary Drivers for Adoption
The transition to sustainable cloud infrastructure is driven by several key factors that align with various SDGs:
- Regulatory Compliance: Mandates such as the EU’s Corporate Sustainability Reporting Directive (CSRD) and SEC climate disclosure rules compel organizations to adopt transparent practices, supporting SDG 16 (Peace, Justice, and Strong Institutions).
- Capital Access and Investment: Institutional investors are increasingly using ESG metrics to assess risk, channeling capital towards companies that demonstrate responsible practices in line with SDG 12 (Responsible Consumption and Production).
- Efficiency and Cost Optimization: A direct correlation exists between carbon efficiency and cost efficiency, where reducing resource waste contributes to both environmental goals and sustainable economic growth under SDG 8 (Decent Work and Economic Growth).
Core Principles of Green Cloud Computing
Foundational Tenets for Sustainability
The practice of green cloud computing is built on principles that directly support the SDGs:
- Energy Efficiency Maximization: Optimizing the entire lifecycle of compute resources to reduce energy consumption, directly contributing to SDG 7 (Affordable and Clean Energy) and SDG 12.
- Sustainable Resource Utilization: Employing renewable energy sources and recyclable materials in infrastructure, which is fundamental to achieving SDG 7 and SDG 13.
- Waste Reduction: Implementing strategies like server virtualization and dynamic resource allocation to minimize electronic and energy waste, aligning with the principles of SDG 12.
Quantifiable Benefits and Contributions to Global Goals
Environmental Impact Reduction
Migrating from on-premise legacy systems to cloud services offers significant environmental benefits:
- A potential reduction in carbon emissions by up to 84%, making a direct contribution to SDG 13 (Climate Action).
- Cloud migrations could collectively reduce annual CO2 emissions by 59 million tons, equivalent to removing 22 million vehicles from service.
Operational and Economic Gains
Sustainable cloud adoption yields measurable improvements in efficiency and financial performance, fostering goals under SDG 8 and SDG 9:
- Server utilization rates can increase from a typical 15-20% to 65-80%.
- Energy consumption per workload can decrease by 30-50%.
- Total cost of ownership (TCO) can be reduced by nearly 50% through lower capital expenditure and operational costs.
Case Studies: Real-World SDG Alignment
UEM Edgenta: Energy Management and Transparent Reporting
Malaysia’s UEM Edgenta utilizes a cloud-based SaaS solution to monitor and optimize carbon emissions. This initiative simplifies carbon accounting and enhances ESG strategy implementation, promoting the transparent reporting required by SDG 12 and SDG 16.
Bharti Airtel: Advancing Clean Energy Adoption
By contracting a 21 MW solar power unit, Bharti Airtel reduced its annual carbon emissions by 25,517 tonnes. This strategic procurement of renewable energy is a clear example of corporate action supporting SDG 7 (Affordable and Clean Energy).
Alibaba: AI-Driven Infrastructure Optimization
The Alibaba Cloud Valley Campus achieved energy consumption reductions of 26% in summer and 10% in winter by using AI algorithms for optimization. This demonstrates an innovative approach to building sustainable infrastructure as envisioned in SDG 9.
The Role of Artificial Intelligence in Green Cloud Computing
AI-Driven Optimization for Environmental Efficiency
Artificial Intelligence is a critical enabler for green cloud computing, contributing to multiple SDGs. AI algorithms can predict energy demand, optimize resource allocation, and improve data center efficiency by up to 40%. These capabilities directly support the efficient use of resources promoted by SDG 7 and SDG 12.
Advanced AI Capabilities for Continuous Optimization
- Predictive Maintenance: AI systems predict equipment failures, reducing electronic waste and supporting SDG 12.
- Generative AI for Code Refactoring: AI tools can optimize legacy code to reduce its computational power requirements, thereby lowering the application’s energy footprint.
- Carbon-Aware Workload Scheduling: AI can schedule non-urgent, intensive tasks to run when renewable energy is most abundant on the grid, maximizing the use of clean power in line with SDG 7.
Strategic Roadmap for Implementing Sustainable Cloud Infrastructure
A phased approach is recommended for enterprises to transition to a sustainable cloud infrastructure that aligns with the SDGs.
- Assess Current Infrastructure: Conduct a comprehensive audit of energy consumption and carbon footprint to establish a baseline.
- Set Clear Sustainability Goals: Define measurable targets linked to specific SDGs, such as reducing emissions (SDG 13) or increasing the use of renewable energy (SDG 7).
- Choose the Right Cloud Partner: Select providers with a demonstrated commitment to sustainability and renewable energy, fostering progress through SDG 17 (Partnerships for the Goals).
- Modernize and Operate: Refactor applications to be carbon-efficient and prioritize serverless or containerized architectures to minimize idle resource consumption.
- Monitor, Measure, and Optimize: Implement tools to track key metrics like Software Carbon Intensity (SCI) and idle resource percentage to ensure continuous improvement.
Future Outlook and Conclusion
The future of green cloud computing will be shaped by emerging technologies like Edge Computing and Software-Defined Power, which will further reduce the environmental impact of digital infrastructure. By adopting green cloud strategies today, organizations can achieve ESG compliance, enhance operational efficiency, and make substantial contributions to the UN Sustainable Development Goals. The imperative is clear for enterprises to transition from legacy systems to sustainable cloud solutions to secure a competitive advantage in a carbon-constrained global economy.
Analysis of Sustainable Development Goals in the Article
1. Which SDGs are addressed or connected to the issues highlighted in the article?
-
SDG 7: Affordable and Clean Energy
- The article extensively discusses the role of green cloud computing in reducing energy consumption and promoting the use of renewable energy sources for powering data centers. It highlights how adopting these technologies leads to greater energy efficiency.
-
SDG 8: Decent Work and Economic Growth
- The text connects sustainable practices with economic benefits, such as reduced operational costs, improved efficiency, and increased business growth. It argues for decoupling economic growth from environmental degradation by showing that “sustainable choices happen to be the most cost-effective choices available.”
-
SDG 9: Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure
- A core theme is the upgrading of legacy IT infrastructure to modern, sustainable, and resilient cloud-based systems. The article emphasizes innovation through technologies like AI, serverless computing, and energy-efficient data centers to create environmentally sound industrial processes.
-
SDG 12: Responsible Consumption and Production
- The article promotes responsible production and consumption patterns within the IT sector. It focuses on maximizing resource efficiency (e.g., server utilization), minimizing waste (e.g., eliminating idle resources), and considering the entire lifecycle of computational resources.
-
SDG 13: Climate Action
- The primary focus of the article is on climate action by reducing the carbon footprint of businesses. It directly addresses the need to cut carbon emissions through technological solutions and aligns corporate strategies with climate-related regulations and disclosure rules.
2. What specific targets under those SDGs can be identified based on the article’s content?
-
SDG 7: Affordable and Clean Energy
- Target 7.2: Increase substantially the share of renewable energy in the global energy mix. The article supports this by mentioning “Renewable energy sources powering your apps” and citing the example of Bharti Airtel, which “strengthened its green energy footprint by contracting a 21 MW solar power unit.”
- Target 7.3: Double the global rate of improvement in energy efficiency. This target is central to the article, which states that green cloud solutions feature “Energy-efficient data centers with advanced cooling systems that use up to 40% less energy” and that “Energy consumption per workload typically decreases by 30-50%.”
-
SDG 8: Decent Work and Economic Growth
- Target 8.4: Improve progressively, through 2030, global resource efficiency in consumption and production and endeavour to decouple economic growth from environmental degradation. The article directly addresses this by stating the goal is to “decouple business growth from carbon intensity” and highlights that “companies can potentially save almost 50% in total cost of ownership” while improving their environmental impact.
-
SDG 9: Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure
- Target 9.4: Upgrade infrastructure and retrofit industries to make them sustainable, with increased resource-use efficiency and greater adoption of clean and environmentally sound technologies. The entire article is a blueprint for this target, advocating for the migration from “Legacy on-premise infrastructure” to sustainable cloud solutions that use AI, server virtualization, and other clean technologies to improve efficiency.
-
SDG 12: Responsible Consumption and Production
- Target 12.2: Achieve the sustainable management and efficient use of natural resources. The article details how green cloud computing achieves this through “dynamic resource allocation” and improving “Server utilization rates from typical 15-20% to 65-80%,” ensuring resources are used efficiently.
- Target 12.5: Substantially reduce waste generation through prevention, reduction, recycling and reuse. The text discusses “Waste cutting strategies,” such as using AI for “predictive maintenance reducing equipment waste” and identifying and eliminating “‘Zombie’ Workloads” which are underutilized servers that consume energy without delivering value.
-
SDG 13: Climate Action
- Target 13.2: Integrate climate change measures into national policies, strategies and planning. While focused on corporate strategy, the article shows how businesses are integrating climate measures in response to regulations like the “EU’s Corporate Sustainability Reporting Directive (CSRD) to the SEC’s climate disclosure rules,” effectively making climate action a part of their core planning.
3. Are there any indicators mentioned or implied in the article that can be used to measure progress towards the identified targets?
-
Indicators for SDG 7
- Renewable Energy Share (Target 7.2): The article provides a specific example that can be used as an indicator: Bharti Airtel’s use of a “21 MW solar power unit.” This represents a measurable quantity of renewable energy capacity added.
- Energy Efficiency Improvement (Target 7.3): The article provides several quantifiable indicators, including a reduction in energy for cooling by “up to 40%,” a decrease in energy consumption per workload by “30-50%,” and Alibaba’s specific energy consumption reduction of “around 26% in summer and 10% in winter.”
-
Indicators for SDG 8
- Resource Efficiency (Target 8.4): A key financial indicator mentioned is the reduction in “total cost of ownership” by “almost 50%,” which measures the economic efficiency gained from sustainable practices. The article also mentions that “AWS workloads are about 4.1 times more efficient than on-premises alternatives,” providing a direct efficiency metric.
-
Indicators for SDG 9
- Sustainable Infrastructure Upgrade (Target 9.4): An indicator of progress is the improvement in “Server utilization rates from typical 15-20% to 65-80%.” This metric directly measures the efficiency gains from upgrading to modern, virtualized infrastructure.
-
Indicators for SDG 12
- Resource Use Efficiency (Target 12.2): The “Idle Resource Percentage” is explicitly mentioned as a “key metric for waste,” which can be tracked to measure the efficiency of resource consumption.
- Waste Reduction (Target 12.5): While not a single number, the practice of identifying and eliminating “‘Zombie’ Workloads” serves as an actionable indicator for reducing electronic and energy waste.
-
Indicators for SDG 13
- Carbon Emission Reduction (Target 13.2): The article is rich with indicators for this target. These include the potential to “cut your carbon emissions by up to 84%,” a total reduction of “59 million tons per year” through cloud migrations, and Bharti Airtel’s specific annual reduction of “25,517 tonnes.” The article also proposes the “Software Carbon Intensity (SCI)” as a precise metric.
4. Create a table with three columns titled ‘SDGs, Targets and Indicators” to present the findings from analyzing the article. In this table, list the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), their corresponding targets, and the specific indicators identified in the article.
| SDGs | Targets | Indicators |
|---|---|---|
| SDG 7: Affordable and Clean Energy | 7.2: Increase share of renewable energy. 7.3: Improve energy efficiency. |
– Share of renewable energy in power mix (e.g., 21 MW solar unit). – Percentage reduction in energy consumption (e.g., 30-50% per workload, 40% for cooling). |
| SDG 8: Decent Work and Economic Growth | 8.4: Improve resource efficiency and decouple growth from environmental degradation. | – Percentage reduction in Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) (e.g., almost 50%). – Operational efficiency improvement factor (e.g., 4.1 times more efficient). |
| SDG 9: Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure | 9.4: Upgrade infrastructure to be sustainable and resource-efficient. | – Server utilization rates (e.g., improvement from 15-20% to 65-80%). – Adoption rate of clean technologies (e.g., AI, serverless architecture). |
| SDG 12: Responsible Consumption and Production | 12.2: Achieve sustainable management and efficient use of natural resources. 12.5: Substantially reduce waste generation. |
– Idle Resource Percentage. – Elimination of “Zombie” workloads. – Reduction in hardware needs through virtualization. |
| SDG 13: Climate Action | 13.2: Integrate climate change measures into policies and strategies. | – Percentage reduction in carbon emissions (e.g., up to 84%). – Absolute reduction in CO2 emissions (e.g., 25,517 tonnes annually). – Software Carbon Intensity (SCI) metric. |
Source: appinventiv.com
What is Your Reaction?
 Like
0
Like
0
 Dislike
0
Dislike
0
 Love
0
Love
0
 Funny
0
Funny
0
 Angry
0
Angry
0
 Sad
0
Sad
0
 Wow
0
Wow
0











































































