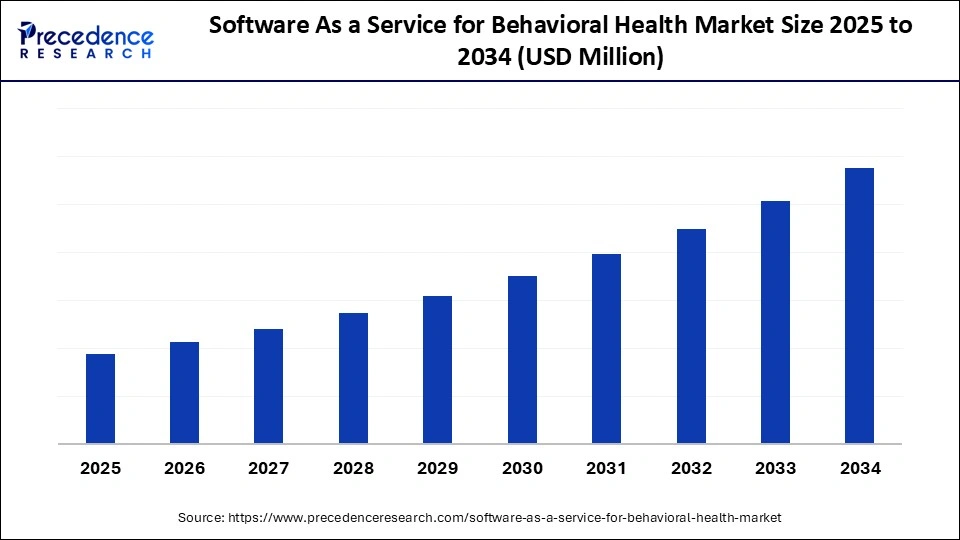
Software as a service for Behavioural Health Market Size, Report by 2034 – Precedence Research
Corporate Profile and Contribution to Sustainable Development Goals
Company Overview
- Headquarters: Austin, Texas, United States
- Year Founded: 1977 (Cerner founded in 1979; acquired by Oracle in 2022)
- Ownership Type: Publicly Traded (NYSE: ORCL)
Historical Context and SDG Alignment
Oracle Corporation, established in 1977, has evolved from a database software company into a global enterprise technology provider. A pivotal development in its strategic direction was the 2022 acquisition of Cerner Corporation for approximately $28 billion. This acquisition firmly positioned Oracle as a key contributor to Sustainable Development Goal 3 (SDG 3): Good Health and Well-being, by integrating advanced health information systems and analytics into its portfolio. The company’s mission is now intrinsically linked to improving global health outcomes through technology.
Key Milestones in Advancing Health and Innovation
- 1977: Oracle Corporation is founded, laying the groundwork for future technological infrastructure.
- 1979: Cerner Corporation is founded, beginning its focus on electronic health records.
- 2004: Oracle launches its initial suite of healthcare enterprise applications.
- 2022: The acquisition of Cerner is completed, marking a significant commitment to advancing SDG 3.
- 2024: The Oracle Health platform is launched, integrating AI and cloud analytics to support behavioral and population health, directly addressing targets within SDG 3.
Strategic Focus on SDG 3: Good Health and Well-being
Business Operations and Health-focused Divisions
Oracle’s operations are structured to support global health initiatives through its Oracle Health (formerly Cerner) division. This segment is dedicated to developing healthcare information systems that enhance clinical workflows, patient engagement, and population health management. These efforts directly support the achievement of SDG 3 by improving the efficiency and accessibility of healthcare services.
Key Offerings for Global Health Improvement
- Oracle Health EHR Platform: Provides foundational digital infrastructure for health systems, a key component for achieving universal health coverage targets under SDG 3.
- Behavioral Health Management Systems: Offers digital tools for case management and treatment planning, addressing the critical need for mental and behavioral health services.
- Population Health Analytics and AI Tools: Enables data-driven public health strategies, contributing to the monitoring and management of community health trends.
- Patient Engagement and Telehealth Platforms: Expands access to care, particularly for remote and underserved populations, directly supporting the goals of SDG 3.
Fostering Innovation and Global Partnerships (SDG 9 & SDG 17)
Technological Capabilities and R&D Focus
Oracle’s commitment to Sustainable Development Goal 9 (SDG 9): Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure is evident in its core technologies. The company leverages its robust cloud infrastructure (OCI), artificial intelligence, and database management expertise to build resilient and innovative healthcare solutions. Its global network of Oracle Labs focuses on AI-driven analytics and data integration to create next-generation health technologies.
Partnerships and Collaborations for the Goals (SDG 17)
In line with Sustainable Development Goal 17 (SDG 17): Partnerships for the Goals, Oracle actively collaborates with a diverse range of stakeholders:
- Partnerships with major healthcare systems to implement integrated behavioral health data management.
- Collaborations with AI firms and academic institutions to advance predictive analytics for improved patient outcomes.
- Alliances with government health agencies to modernize population health infrastructure and support public health initiatives.
Recent Innovations and Product Launches
- Oracle Health EHR Behavioral Module (2023): A targeted solution to improve mental healthcare delivery.
- AI-based Patient Risk Stratification Tools (2024): An innovation supporting preventative care and efficient resource allocation in health systems.
- Oracle Cloud Data Platform for Healthcare (2025): A platform designed to enhance data interoperability, a critical element for a modern healthcare infrastructure as envisioned by SDG 9.
Global Operations and Financial Performance
Geographic Presence
Oracle’s extensive global presence, serving customers in over 175 countries, provides a platform to scale its health technology solutions worldwide. This reach is instrumental in disseminating innovations that can help nations achieve their health and technology-related SDG targets.
Financial Overview
With annual revenues of approximately $52 billion USD, Oracle demonstrates significant financial capacity to invest in research and development for healthcare technology. The growing revenue contribution from its cloud and healthcare segments, accelerated by the Cerner acquisition, underscores the strategic and financial commitment to advancing global health solutions.
Strategic Analysis and Future Outlook
Competitive Positioning
- Strengths: A strong enterprise cloud foundation and global reach, enabling the deployment of scalable solutions that support SDG 3 and SDG 9.
- Differentiators: A unified healthcare data platform that combines cloud, AI, and EHR capabilities to offer a comprehensive approach to health system modernization.
SWOT Analysis in the Context of Sustainable Development
- Strengths: Global brand recognition and deep expertise in data management, which are critical for large-scale health information projects.
- Weaknesses: The complexity of integrating legacy systems presents a challenge to the rapid deployment of unified health platforms.
- Opportunities: Significant potential for expansion in behavioral health analytics and cloud-based systems, directly aligning with underserved areas of SDG 3.
- Threats: Intense competition from specialized EHR providers could impact market share and the pace of adoption.
Recent Developments and Future Commitments
Recent activities underscore Oracle’s continued focus on integrating technology with healthcare to meet global challenges:
- May 2024: Launch of an AI-powered behavioral health clinical workflow module.
- September 2024: Opening of a new healthcare innovation hub to foster collaboration and development.
- January 2025: Announcement of collaborations to expand cloud-based behavioral health data platforms, reinforcing the company’s commitment to SDG 3, SDG 9, and SDG 17.
Analysis of Sustainable Development Goals in the Article
1. Which SDGs are addressed or connected to the issues highlighted in the article?
-
SDG 3: Good Health and Well-being
- The article’s primary focus is on Oracle’s expansion into healthcare technology through its acquisition of Cerner. It details the development of solutions for electronic health records (EHR), behavioral health, population health management, and patient engagement, all of which are central to ensuring healthy lives and promoting well-being.
-
SDG 9: Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure
- The article highlights Oracle’s significant investment in technology and innovation, such as cloud infrastructure, AI, and data analytics. The development of a “unified data architecture across health systems,” R&D centers, and an “innovation hub” directly relates to building resilient infrastructure and fostering innovation.
-
SDG 17: Partnerships for the Goals
- The article explicitly mentions Oracle’s strategy of forming partnerships to achieve its objectives. It details “Partnerships with major healthcare systems,” “Collaborations with AI firms and universities,” and “Alliances with government health agencies,” which exemplify the multi-stakeholder collaborations needed to advance sustainable development.
2. What specific targets under those SDGs can be identified based on the article’s content?
-
Under SDG 3: Good Health and Well-being
- Target 3.4: Promote mental health and well-being. The article repeatedly emphasizes Oracle’s focus on “behavioral health,” including the launch of an “integrated behavioral health EHR module” and “AI-powered behavioral health clinical workflow module.” These tools are designed to improve the treatment and management of mental health conditions.
- Target 3.8: Achieve universal health coverage, including access to quality essential health-care services. Oracle’s development of EHR platforms, “tele-behavioral health,” and “remote patient monitoring” aims to improve the efficiency, accessibility, and quality of healthcare services by enhancing clinical workflows and patient engagement.
- Target 3.d: Strengthen the capacity for early warning, risk reduction, and management of health risks. The article mentions the launch of the “Oracle Health Data Intelligence platform integrating AI for population and behavioral health analytics” and “AI-based patient risk stratification and decision support tools,” which directly contribute to strengthening the capacity to manage population health risks through predictive analytics.
-
Under SDG 9: Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure
- Target 9.5: Enhance scientific research and upgrade technological capabilities. The article details Oracle’s “R&D Focus” on “AI-driven healthcare analytics, data integration, and patient engagement technologies.” The establishment of a “healthcare innovation hub” and collaborations with universities are direct efforts to enhance research and upgrade technological capabilities in the healthcare industry.
-
Under SDG 17: Partnerships for the Goals
- Target 17.16 & 17.17: Enhance the global partnership for sustainable development and encourage effective public, public-private, and civil society partnerships. The article describes Oracle’s strategy of forming “Alliances with government health agencies for population health modernization” (public-private partnerships) and “Collaborations with AI firms and universities” (multi-stakeholder partnerships) to share knowledge and technology to advance healthcare solutions.
3. Are there any indicators mentioned or implied in the article that can be used to measure progress towards the identified targets?
-
For SDG 3 (Good Health and Well-being)
- The article implies progress can be measured by the development and adoption of specific health technologies. Implied indicators include the number of healthcare systems adopting the “Oracle Health EHR Platform,” the deployment of the “integrated behavioral health EHR module,” and the utilization rates of “telehealth platforms” and “remote patient monitoring” capabilities. Improved “population health outcomes” is mentioned as a goal, which itself is a high-level indicator.
-
For SDG 9 (Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure)
- Progress towards innovation can be measured by the specific product launches and infrastructure developments mentioned. Indicators implied in the text include the number of “Product Launches / Innovations” such as the “AI-based patient risk stratification tools,” the establishment of new “R&D centers” or “innovation hubs,” and the scale of investment in “cloud infrastructure” dedicated to healthcare.
-
For SDG 17 (Partnerships for the Goals)
- The article suggests that progress can be tracked by the formation and scope of collaborative efforts. Measurable indicators would be the number of “Partnerships with major healthcare systems,” the number of “Collaborations with AI firms and universities,” and the quantity and scale of “Alliances with government health agencies” that are established.
Summary of Findings
| SDGs | Targets | Indicators (Mentioned or Implied in the Article) |
|---|---|---|
| SDG 3: Good Health and Well-being |
|
|
| SDG 9: Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure |
|
|
| SDG 17: Partnerships for the Goals |
|
|
Source: precedenceresearch.com
What is Your Reaction?
 Like
0
Like
0
 Dislike
0
Dislike
0
 Love
0
Love
0
 Funny
0
Funny
0
 Angry
0
Angry
0
 Sad
0
Sad
0
 Wow
0
Wow
0











































































