ACCA publishes global study on corporate sustainability reporting progress – Vietnam Investment Review – VIR
Global Progress on Corporate Sustainability Reporting and Alignment with Sustainable Development Goals
Introduction
A global study by the Association of Chartered Certified Accountants (ACCA), titled “Sustainability reporting: Track your progress to create decision-useful information,” assesses corporate readiness for sustainability reporting. Based on input from over 1,000 professionals across 113 jurisdictions, the research underscores that integrating sustainability into core operations is critical for achieving long-term resilience and contributing to the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs).
Key Findings on Corporate Integration of SDGs
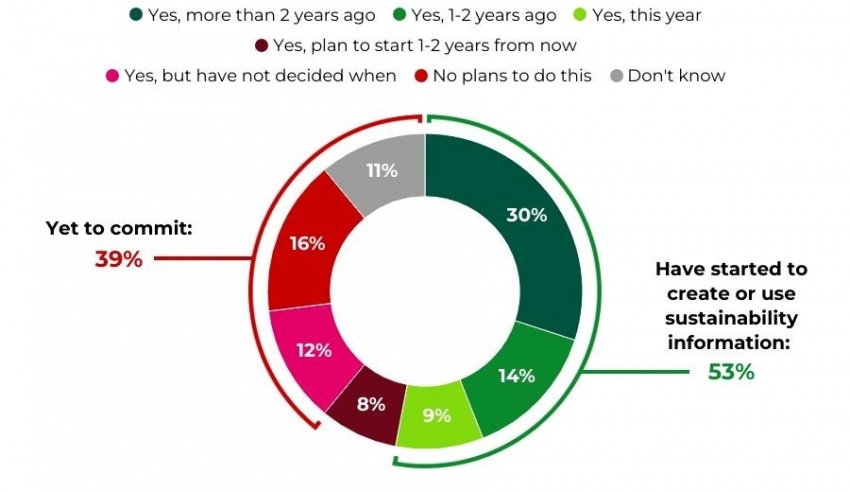
The report reveals uneven progress in the adoption of sustainable practices, which is fundamental to achieving goals such as SDG 12 (Responsible Consumption and Production). Key statistics include:
- Uneven Adoption: While 53% of surveyed organisations have begun creating or using sustainability information, a significant 39% have yet to make any commitment to sustainability reporting.
- Leadership and Strategy Gap: Only 16% of senior management and boards currently use sustainability insights for major business decisions. This indicates a disconnect between data collection and strategic implementation, hindering progress towards SDG 8 (Decent Work and Economic Growth) and SDG 9 (Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure).
- Lack of Integration: For many organisations, sustainability remains a parallel activity rather than a core component of business strategy, limiting its potential to drive meaningful contributions to the 2030 Agenda.
Challenges and Drivers in SDG-Aligned Reporting
Organisations face several challenges and are influenced by specific drivers in their journey towards comprehensive sustainability reporting.
- Operational Challenges: Many companies struggle to identify critical resources and assess the information needs of diverse stakeholders. This impedes their ability to report effectively on their environmental and social impacts, a key requirement of SDG 12.6, which encourages companies to integrate sustainability information into their reporting cycles.
- Regulatory Motivation: Regulatory requirements are a primary driver, cited by 71% of respondents. However, a compliance-only focus is insufficient, as it overlooks opportunities to enhance decision-making, attract investment, and build stakeholder trust, which are crucial for supporting SDG 16 (Peace, Justice, and Strong Institutions).
- Leadership as a Determinant: The report identifies leadership commitment as the most critical factor for progress. Active executive and board-level responsibility for sustainability outcomes drives investment in the necessary systems, processes, and skills for credible reporting.
Strategic Recommendations for Advancing the 2030 Agenda
To accelerate progress, the ACCA report advocates for several strategic actions that align with the SDGs:
- Adopt Global Standards: The adoption of globally consistent standards, such as those from the International Sustainability Standards Board (ISSB), is essential. This enhances the comparability and credibility of reports, fostering investor confidence and supporting a global framework for sustainable development.
- Foster Cross-Sector Collaboration: The report highlights that partnerships across industries and regions are vital. Such collaboration directly supports SDG 17 (Partnerships for the Goals) by enabling businesses to share best practices, overcome resource constraints, and align reporting frameworks.
- Leverage Professional Accountants: Accountants are positioned to bridge the gap between sustainability and finance. Their expertise in measurement, governance, and assurance can help create decision-useful information that drives strategic action toward achieving all SDGs.
Conclusion: Sustainability as a Core Component for Global Goals
The ACCA report concludes that sustainability information is no longer an optional add-on but a central element of modern business strategy. The integration of sustainability and financial considerations is a growing necessity for organisational resilience, creating sustainable profits, and making a tangible contribution to the global Sustainable Development Goals. This strategic alignment is crucial for addressing risks and seizing opportunities related to environmental, social, and governance factors.
Analysis of Sustainable Development Goals in the Article
1. Which SDGs are addressed or connected to the issues highlighted in the article?
-
SDG 12: Responsible Consumption and Production
- The article’s central theme is corporate sustainability reporting, which is a core component of responsible production. It discusses how businesses track, report, and integrate sustainability information into their operations to manage their impact on the environment and society. The focus on making sustainability a core part of business strategy rather than a parallel activity directly relates to promoting sustainable practices within companies.
-
SDG 17: Partnerships for the Goals
- The article explicitly highlights the importance of collaboration to advance sustainability reporting. It mentions that “stronger cross-sector collaboration” and “partnerships across industries and regions” are beneficial for sharing best practices, overcoming resource constraints, and aligning reporting frameworks with international standards. This directly supports the idea of building partnerships to achieve sustainable development.
-
SDG 8: Decent Work and Economic Growth
- The article connects sustainable business practices to “organisational resilience,” “long-term success,” and the ability to “create sustainable value.” By integrating sustainability, companies can better manage risks, attract investment, and ensure their long-term viability, which contributes to stable and sustainable economic growth. The discussion on improving decision-making through sustainability data supports the development of more resilient and efficient economic models.
2. What specific targets under those SDGs can be identified based on the article’s content?
-
Target 12.6: Encourage companies, especially large and transnational companies, to adopt sustainable practices and to integrate sustainability information into their reporting cycle.
- This target is the primary focus of the article. The ACCA research paper, “Sustainability reporting: Track your progress to create decision-useful information,” directly assesses the progress of companies in adopting and integrating sustainability reporting. The article details the percentage of organizations using this information (53%) and the challenges they face, which is a direct evaluation of progress toward this target.
-
Target 17.16: Enhance the global partnership for sustainable development, complemented by multi-stakeholder partnerships that mobilize and share knowledge, expertise, technology and financial resources, to support the achievement of the sustainable development goals in all countries, in particular developing countries.
- The article’s advocacy for “globally consistent standards” and its finding that “30 per cent of respondents reported benefiting from partnerships across industries and regions to enhance reporting capabilities” directly align with this target. It emphasizes sharing knowledge and best practices through collaboration to improve sustainability outcomes globally.
-
Target 8.4: Improve progressively, through 2030, global resource efficiency in consumption and production and endeavour to decouple economic growth from environmental degradation…
- The article implies this target by stating that at the core of useful sustainability information is an “appreciation of the factors… that can affect the resources an organisation depends upon.” By improving sustainability reporting, companies can better manage their resource use, identify inefficiencies, and mitigate environmental impacts, thus contributing to greater resource efficiency and decoupling growth from degradation.
3. Are there any indicators mentioned or implied in the article that can be used to measure progress towards the identified targets?
-
For Target 12.6:
- Percentage of organizations creating or using sustainability information: The article explicitly states that “Just over half of surveyed organisations (53 per cent) have begun to create or use sustainability information.” This is a direct quantitative indicator of the adoption of sustainability reporting.
- Percentage of senior management using sustainability insights for decision-making: The article provides the statistic that “only 16 per cent of senior management and boards currently use these insights to guide major business decisions.” This indicator measures the depth of integration of sustainability information into core business strategy.
- Adoption of international sustainability standards: The article mentions the importance of adopting standards from the “International Sustainability Standards Board” to enhance comparability and credibility. The rate of adoption of such standards by companies serves as a qualitative and quantitative indicator of progress.
-
For Target 17.16:
- Percentage of organizations benefiting from cross-sector partnerships: The article provides a clear indicator by stating, “About 30 per cent of respondents reported benefiting from partnerships across industries and regions to enhance reporting capabilities.” This measures the effectiveness and reach of collaborative efforts in the field of sustainability reporting.
SDGs, Targets, and Indicators Table
| SDGs | Targets | Indicators |
|---|---|---|
| SDG 12: Responsible Consumption and Production | Target 12.6: Encourage companies to adopt sustainable practices and integrate sustainability information into their reporting cycle. |
|
| SDG 17: Partnerships for the Goals | Target 17.16: Enhance the global partnership for sustainable development, complemented by multi-stakeholder partnerships. |
|
| SDG 8: Decent Work and Economic Growth | Target 8.4: Improve global resource efficiency in consumption and production. |
|
Source: vir.com.vn
What is Your Reaction?
 Like
0
Like
0
 Dislike
0
Dislike
0
 Love
0
Love
0
 Funny
0
Funny
0
 Angry
0
Angry
0
 Sad
0
Sad
0
 Wow
0
Wow
0













































































