SUSTAINABLE PLANET- VISION 2030
Call to action to end poverty and inequality, protect the planet, and ensure that all people enjoy health and well-being. The Sustainable Development Goals are a call for action by all countries — poor, rich and middle-income — to promote prosperity while protecting the planet. They recognize that ending poverty must go hand-in-hand with strategies that build economic growth and address a range of social needs including education, health, social protection, and job opportunities, while tackling climate change and environmental protection.

ABSTRACT
Imagine you are in a world with no trees around, no life forms and filled with pollutants making the earth look barren. How would you feel? Instead of this, the United Nations has adopted an environmental scheme known as Global Goals or Sustainable Developmental Goals. (SDGs). This scheme is” a development that meets the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs.” It conveys social, economic, and environmental issues.
SDG Spotlight: Goals 13, 14, and 15
Take urgent action to combat climate change and its impacts. Conserve and sustainably use the oceans, seas and marine resources. Sustainably manage forests, combat desertification, halt and reverse land degradation, halt biodiversity loss.
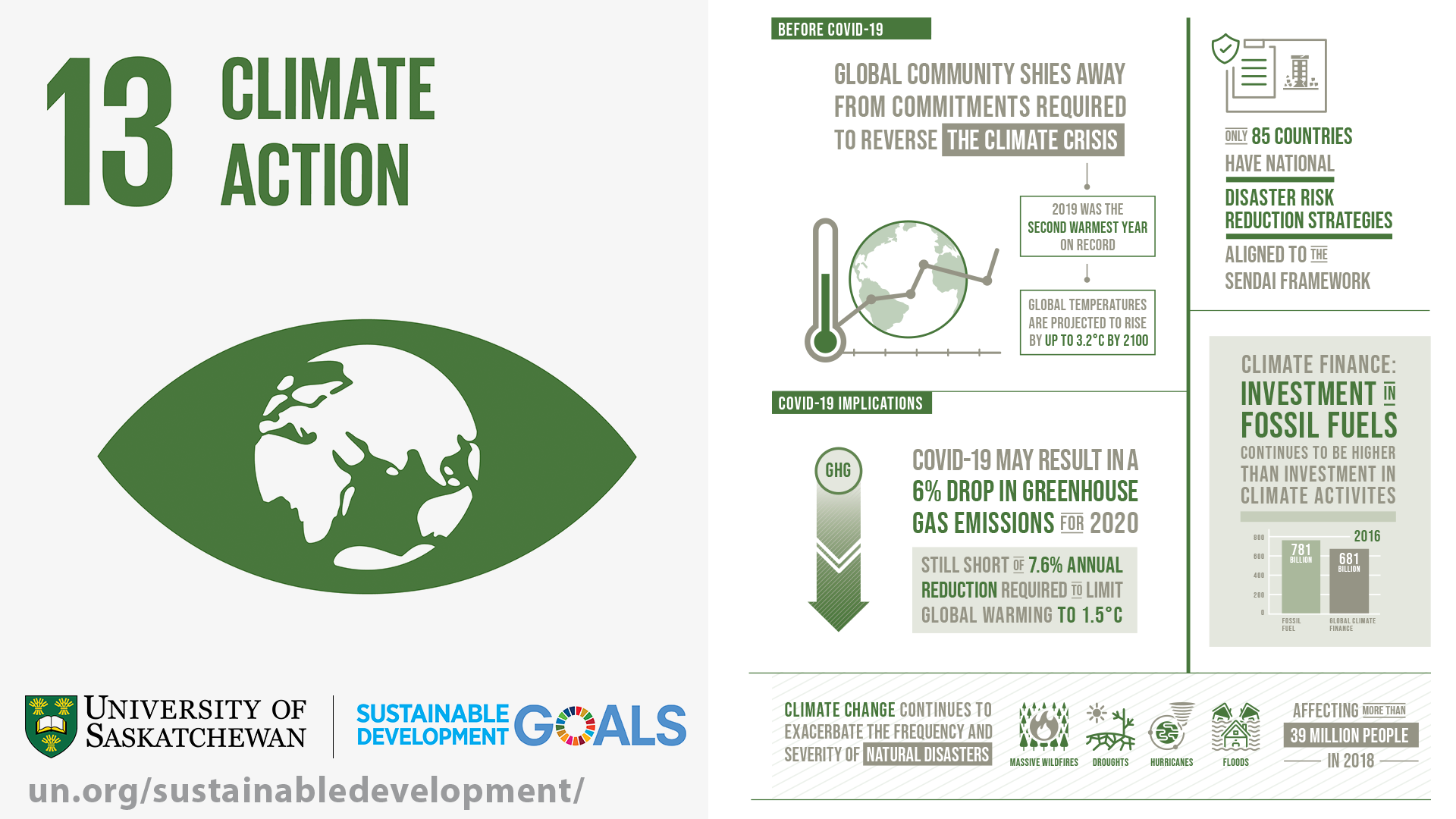
2019 was the second warmest year on record and the end of the warmest decade (2010- 2019) ever recorded.
Carbon dioxide (CO2) levels and other greenhouse gases in the atmosphere rose to new records in 2019.
Climate change is affecting every country on every continent. It is disrupting national economies and affecting lives. Weather patterns are changing, sea levels are rising, and weather events are becoming more extreme.
Although greenhouse gas emissions are projected to drop about 6 per cent in 2020 due to travel bans and economic slowdowns resulting from the COVID-19 pandemic, this improvement is only temporary. Climate change is not on pause. Once the global economy begins to recover from the pandemic, emissions are expected to return to higher levels.
Saving lives and livelihoods requires urgent action to address both the pandemic and the climate emergency.
The Paris Agreement, adopted in 2015, aims to strengthen the global response to the threat of climate change by keeping a global temperature rise this century well below 2 degrees Celsius above pre-industrial levels. The agreement also aims to strengthen the ability of countries to deal with the impacts of climate change, through appropriate financial flows, a new technology framework and an enhanced capacity building framework.
The ocean drives global systems that make the Earth habitable for humankind. Our rainwater, drinking water, weather, climate, coastlines, much of our food, and even the oxygen in the air we breathe, are all ultimately provided and regulated by the sea.
Careful management of this essential global resource is a key feature of a sustainable future. However, at the current time, there is a continuous deterioration of coastal waters owing to pollution, and ocean acidification is having an adversarial effect on the functioning of ecosystems and biodiversity. This is also negatively impacting small scale fisheries.
Saving our ocean must remain a priority. Marine biodiversity is critical to the health of people and our planet. Marine protected areas need to be effectively managed and well-resourced and regulations need to be put in place to reduce overfishing, marine pollution and ocean acidification.

Nature is critical to our survival: nature provides us with our oxygen, regulates our weather patterns, pollinates our crops, produces our food, feed and fibre. But it is under increasing stress. Human activity has altered almost 75 per cent of the earth’s surface, squeezing wildlife and nature into an ever-smaller corner of the planet.
Around 1 million animal and plant species are threatened with extinction – many within decades – according to the 2019 Global Assessment Report on Biodiversity and Ecosystem Service. The report called for transformative changes to restore and protect nature. It found that the health of ecosystems on which we and all other species depend is deteriorating more rapidly than ever, affecting the very foundations of our economies, livelihoods, food security, health and quality of life worldwide.
Deforestation and desertification – caused by human activities and climate change – pose major challenges to sustainable development and have affected the lives and livelihoods of millions of people. Forests are vitally important for sustaining life on Earth, and play a major role in the fight against climate change. And investing in land restoration is critical for improving livelihoods, reducing vulnerabilities, and reducing risks for the economy.

The health of our planet also plays an important role in the emergence of zoonotic diseases, i.e. diseases that are transmissible between animals and humans. As we continue to encroach on fragile ecosystems, we bring humans into ever-greater contact with wildlife, enabling pathogens in wildlife to spill over to livestock and humans, increasing the risk of disease emergence and amplification.
https://www.un.org/sustainabledevelopment/development-agenda/
What is Your Reaction?
 Like
1
Like
1
 Dislike
0
Dislike
0
 Love
0
Love
0
 Funny
0
Funny
0
 Angry
0
Angry
0
 Sad
0
Sad
0
 Wow
0
Wow
0














































































