U.S. Water and Wastewater Treatment Technologies Market: Growth Outlook, Trends, and Future Opportunities – openPR.com
Report on the U.S. Water and Wastewater Treatment Market and its Contribution to Sustainable Development Goals
Executive Summary
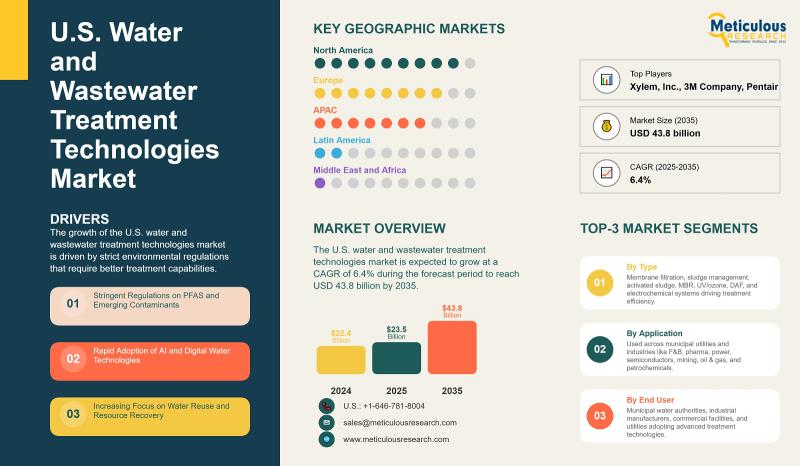
The United States water and wastewater treatment technologies market is undergoing significant expansion, driven by regulatory mandates, infrastructure renewal, and the urgent need for sustainable water management. This growth directly supports the achievement of several United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), most notably SDG 6 (Clean Water and Sanitation), SDG 9 (Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure), and SDG 12 (Responsible Consumption and Production). The market, valued at USD 22.4 billion in 2024, is projected to reach USD 43.8 billion by 2035, reflecting a 6.4% CAGR. This report analyzes the market’s key drivers, technological advancements, and industrial trends through the lens of the SDGs.
Market Drivers and Alignment with Global Sustainability Targets
Regulatory Frameworks and Infrastructure Investment Supporting SDG 6 and SDG 9
The market’s growth is fundamentally linked to policies aimed at ensuring universal access to clean water and building resilient infrastructure.
- SDG 6: Clean Water and Sanitation: Strict federal and state regulations, including the EPA’s 2024 PFAS standards, are compelling over 5,000 water systems to upgrade their treatment capabilities. This initiative is a direct action towards achieving Target 6.1 (safe drinking water) and Target 6.3 (improving water quality by reducing pollution).
- SDG 9: Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure: Federal infrastructure programs have allocated over USD 50 billion for water-related projects through 2032. These investments focus on modernizing municipal systems and adopting advanced technologies, contributing to Target 9.1 (develop quality, reliable, sustainable, and resilient infrastructure).
Climate Change and Water Scarcity as Catalysts for SDG 13 and SDG 12
Environmental pressures are accelerating the adoption of technologies that promote water efficiency and reuse.
- SDG 13: Climate Action: Increasing water scarcity in several U.S. regions, exacerbated by climate change, is driving demand for water reuse and recycling technologies. This aligns with efforts to build resilience to climate-related hazards.
- SDG 12: Responsible Consumption and Production: The push for sustainable and cost-effective water management has increased the adoption of membrane systems, energy-efficient filtration, and advanced sludge management, supporting sustainable consumption and production patterns.
Technological Advancements Fostering Innovation and Sustainability (SDG 9)
Dominance of Membrane Separation Technologies
Membrane technologies are central to achieving water quality goals due to their high efficiency and adaptability. Their continued development supports SDG 9 by fostering technological innovation.
- High Efficiency: Technologies like reverse osmosis, ultrafiltration, and nanofiltration are highly effective at removing emerging contaminants, directly contributing to SDG 6.
- Energy Efficiency: Advances in membrane durability and lower energy requirements make these solutions more sustainable and accessible, aligning with SDG 12.
- Industrial Application: Their ability to produce ultrapure water is critical for sustainable industrial growth in sectors like semiconductors and data centers (SDG 9).
Emerging and Digital Solutions
Innovation extends beyond membranes to include a suite of advanced and digital tools that optimize water management.
- Advanced Treatment Systems: Membrane bioreactors (MBRs), UV disinfection, and ozone systems offer improved performance and lower operational costs.
- Digital Water Management: The adoption of real-time monitoring, predictive maintenance, and automated control systems helps reduce energy and chemical consumption, enhancing operational efficiency and supporting SDG 6 and SDG 12.
Industrial Sector Growth and Commitment to Responsible Production (SDG 12)
High-Growth Industries Driving Demand
The industrial segment is projected to be the fastest-growing sector, with its expansion tied to sustainable water practices.
- Semiconductors and Data Centers: Fueled by federal initiatives like the CHIPS Act, these industries require vast amounts of ultrapure water and generate significant wastewater, necessitating advanced treatment and recycling technologies.
- Other Key Sectors: Battery manufacturing, pharmaceuticals, mining, and energy industries are increasingly adopting high-performance filtration to meet regulatory standards and sustainability goals.
Adoption of Sustainable Water Management Practices
Industries are actively implementing systems that contribute to SDG 12 by minimizing environmental impact.
- Zero-Liquid-Discharge (ZLD) Systems: These systems eliminate liquid waste discharge, a key goal for responsible industrial production.
- Water Reuse and Recycling: Widespread adoption of these practices reduces the strain on freshwater resources, directly supporting Target 6.4 (substantially increase water-use efficiency).
Competitive Landscape and Strategic Alignment with SDGs
Corporate Strategies Reflecting Sustainability Goals
Major market players are positioning themselves to address global water challenges through strategic mergers, acquisitions, and innovation.
- Xylem’s Acquisition of Evoqua: This 2023 merger created the largest pure-play water technology company, enhancing its capacity to deliver comprehensive solutions for municipal and industrial clients in line with SDG 6 and SDG 9.
- DuPont’s Focus on Water Solutions: By retaining its Water Solutions division, DuPont is reinforcing its commitment to developing advanced reverse osmosis and PFAS treatment technologies.
- 3M’s Transition: The company’s commitment to cease PFAS manufacturing by 2025 and invest in new remediation technologies demonstrates a corporate shift towards environmental responsibility (SDG 12).
- Venture Capital Investment: Increased funding for startups developing PFAS destruction technologies and AI-driven management solutions accelerates the innovation needed to achieve the SDGs.
Analysis of Sustainable Development Goals in the Article
1. Which SDGs are addressed or connected to the issues highlighted in the article?
The article on the U.S. Water and Wastewater Treatment Technologies Market addresses several Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) by focusing on environmental protection, infrastructure development, technological innovation, and public health. The following SDGs are directly connected to the issues discussed:
- SDG 6: Clean Water and Sanitation: This is the most prominent SDG in the article. The entire text revolves around technologies and market trends aimed at ensuring the availability and sustainable management of water and sanitation. It discusses the rising demand for “clean and reusable water,” “wastewater management solutions,” and the challenges of maintaining “water quality.”
- SDG 9: Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure: The article extensively covers the need to upgrade “aging infrastructure” and invest in new, resilient systems. It highlights “advancements in treatment technologies” like membrane separation and digital water management tools. Furthermore, it connects the growth of the water treatment market to industrial expansion in sectors such as semiconductors, pharmaceuticals, and data centers, which require innovative water solutions.
- SDG 11: Sustainable Cities and Communities: The focus on “municipal systems” and the impact of regulations on “more than 5,000 water systems nationwide” directly relates to making cities and human settlements inclusive, safe, resilient, and sustainable. Modernizing municipal water infrastructure is a core component of providing essential services to urban populations.
- SDG 12: Responsible Consumption and Production: The article emphasizes sustainable practices such as “water reuse and recycling technologies” and “zero-liquid-discharge systems.” It also addresses the environmentally sound management of hazardous chemicals through its detailed discussion of the new EPA regulations for PFAS (“forever chemicals”) and corporate actions to phase out their production.
2. What specific targets under those SDGs can be identified based on the article’s content?
Based on the article’s content, several specific SDG targets can be identified:
- Target 6.3: By 2030, improve water quality by reducing pollution, eliminating dumping and minimizing release of hazardous chemicals and materials, halving the proportion of untreated wastewater and substantially increasing recycling and safe reuse globally.
- Explanation: The article’s focus on the EPA’s new standards for PFAS, which set “strict limits for several PFAS compounds,” and the resulting demand for “PFAS removal technologies” directly aligns with reducing pollution from hazardous chemicals. The discussion of “advanced sludge management solutions” and wastewater treatment also contributes to this target.
- Target 9.1: Develop quality, reliable, sustainable and resilient infrastructure, including regional and transborder infrastructure, to support economic development and human well-being, with a focus on affordable and equitable access for all.
- Explanation: The article highlights that federal infrastructure programs have committed over “USD 50 billion for water-related projects,” prioritizing the “modernization of municipal systems” and the “replacement of outdated pipelines.” This directly addresses the goal of developing sustainable and resilient infrastructure.
- Target 9.4: By 2030, upgrade infrastructure and retrofit industries to make them sustainable, with increased resource-use efficiency and greater adoption of clean and environmentally sound technologies and industrial processes.
- Explanation: The article describes industries adopting “zero-liquid-discharge technologies, water reuse systems, and high-performance filtration solutions.” It also points to the development of “energy-efficient filtration units” and “digital water management tools” that reduce energy consumption and optimize chemical usage, which is central to this target.
- Target 12.2: By 2030, achieve the sustainable management and efficient use of natural resources.
- Explanation: The rising demand for “water reuse and recycling technologies” driven by “climate change and rising water scarcity” is a direct response to the need for more efficient use of water, a critical natural resource.
- Target 12.4: By 2020, achieve the environmentally sound management of chemicals and all wastes throughout their life cycle… and significantly reduce their release to air, water and soil to minimize their adverse impacts on human health and the environment.
- Explanation: The article’s detailed coverage of the new regulations for PFAS, a group of hazardous “forever chemicals,” and the corporate response, such as 3M’s commitment to “ending PFAS manufacturing by 2025,” directly relates to the sound management of chemicals to protect water resources and public health.
3. Are there any indicators mentioned or implied in the article that can be used to measure progress towards the identified targets?
Yes, the article contains several quantitative and qualitative indicators that can be used to measure progress towards the identified targets:
- Financial Investment in Infrastructure (Target 9.1): The article states that “Federal infrastructure investment programs committed over USD 50 billion for water-related projects through 2032.” This monetary value serves as a direct indicator of investment in sustainable infrastructure.
- Market Growth for Clean Technologies (Target 9.4): The market for water and wastewater treatment technologies is projected to grow from “USD 22.4 billion in 2024” to “USD 43.8 billion by 2035,” with a “CAGR of 6.4%.” This growth rate indicates an increasing adoption of environmentally sound technologies.
- Regulatory Compliance Scope (Target 6.3 & 12.4): The EPA’s new PFAS standards affect “more than 5,000 water systems nationwide.” The number of systems that achieve compliance by the 2031 deadline can be used as an indicator of progress in reducing chemical pollution.
- Corporate Action on Hazardous Chemicals (Target 12.4): The commitment by 3M to “end PFAS manufacturing by 2025” is a specific, measurable corporate action towards the environmentally sound management of chemicals.
- Adoption of Sustainable Industrial Processes (Target 9.4 & 12.2): The article notes that fast-growing industrial sectors (semiconductors, data centers, battery manufacturing) are “increasingly adopting zero-liquid-discharge technologies, water reuse systems, and high-performance filtration solutions.” The rate of adoption of these systems can serve as an indicator of increased resource-use efficiency.
- Technological Innovation and Investment (Target 9.4): The article mentions that “venture investments are accelerating breakthroughs” and that “Xylem has also expanded its venture fund to USD 50 million to support emerging technologies.” This investment in R&D is an indicator of progress in developing cleaner and more efficient technologies.
4. Summary Table of SDGs, Targets, and Indicators
| SDGs | Targets | Indicators Identified in the Article |
|---|---|---|
| SDG 6: Clean Water and Sanitation | Target 6.3: Improve water quality by reducing pollution and minimizing the release of hazardous chemicals. |
|
| SDG 9: Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure |
Target 9.1: Develop quality, reliable, sustainable and resilient infrastructure.
Target 9.4: Upgrade infrastructure and retrofit industries to make them sustainable and resource-efficient. |
|
| SDG 11: Sustainable Cities and Communities | Target 11.1: Ensure access for all to adequate, safe and affordable basic services. |
|
| SDG 12: Responsible Consumption and Production |
Target 12.2: Achieve the sustainable management and efficient use of natural resources.
Target 12.4: Achieve the environmentally sound management of chemicals and all wastes. |
|
Source: openpr.com
What is Your Reaction?
 Like
0
Like
0
 Dislike
0
Dislike
0
 Love
0
Love
0
 Funny
0
Funny
0
 Angry
0
Angry
0
 Sad
0
Sad
0
 Wow
0
Wow
0














































































