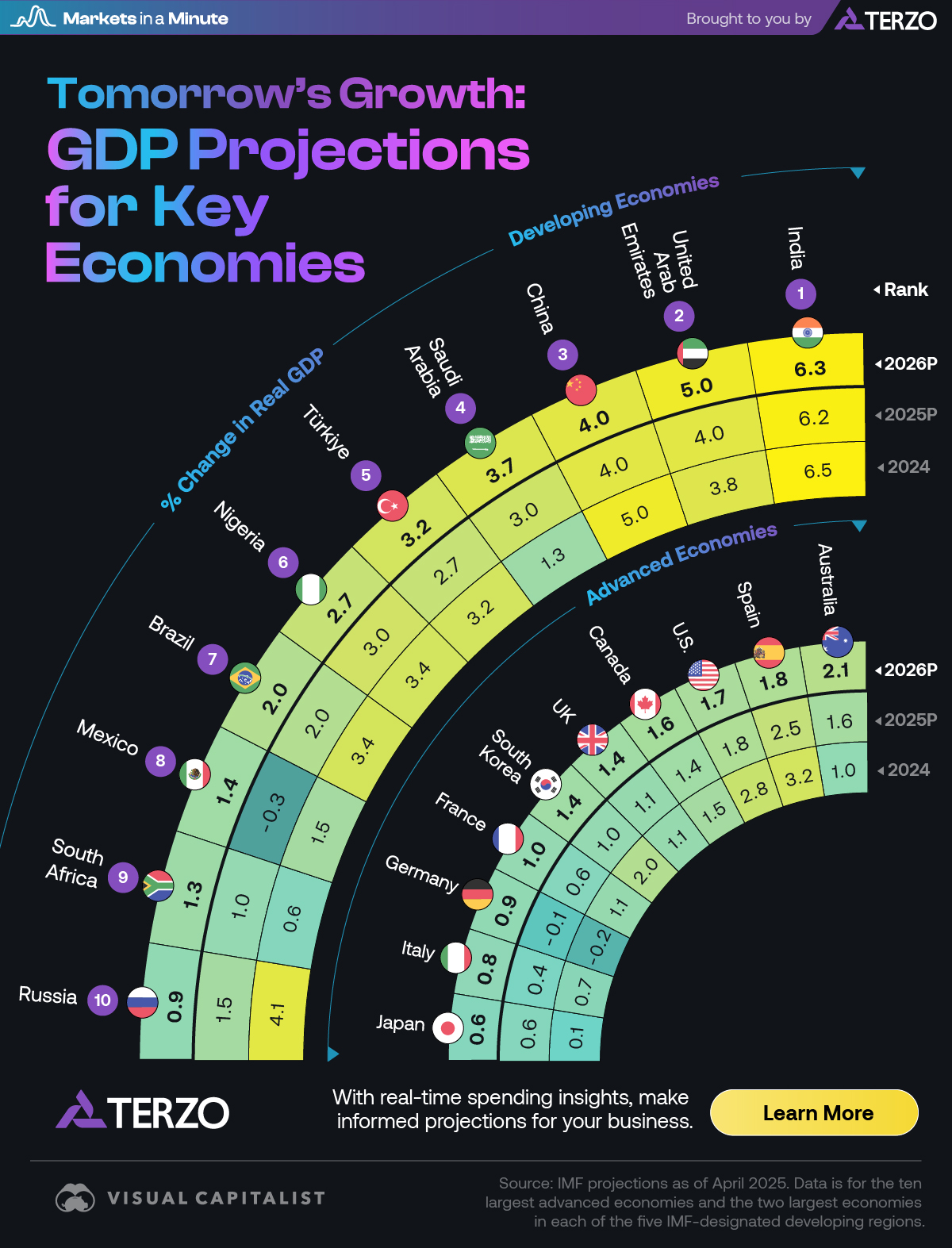
Without data centers, GDP growth was 0.1% in the first half of 2025, Harvard economist says – Fortune
Analysis of U.S. Economic Growth in H1 2025 and Alignment with Sustainable Development Goals
Economic Performance and Contribution Analysis
An assessment of United States economic performance in the first half of 2025 reveals a heavy reliance on a single sector for growth, raising questions about its alignment with SDG 8: Decent Work and Economic Growth, which emphasizes inclusive and sustainable economic development. According to analysis by Harvard economist Jason Furman, investment in data centers and information processing technology was the primary driver of GDP expansion.
- Excluding technology-related investments, annualized GDP growth would have been a near-stagnant 0.1%.
- Investment in information-processing equipment and software constituted only 4% of U.S. GDP but accounted for 92% of its growth during this period.
- For the first time, the contribution to GDP growth from AI data-center construction surpassed that of U.S. consumer spending, a sector that traditionally comprises two-thirds of the economy.
This concentration of growth in a narrow segment of the economy suggests a potential vulnerability and a lack of the broad-based, inclusive progress targeted by SDG 8.
Implications for SDG 9: Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure
The massive capital expenditure on high-tech infrastructure directly corresponds with the objectives of SDG 9: Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure. The goal to build resilient infrastructure and foster innovation is being advanced by significant corporate investment.
- Major technology firms including Microsoft, Google, Amazon, Meta, and Nvidia have invested tens of billions of dollars into data center construction and upgrades.
- Lisa Shallet of Morgan Stanley Wealth Management noted that capital expenditure by “hyperscalers” on data centers and related infrastructure has quadrupled, approaching $400 billion annually.
- This spending is estimated to add approximately 100 basis points to U.S. real GDP growth.
While this buildout represents a significant leap in digital infrastructure, concerns about an “industrial bubble,” as termed by Jeff Bezos, question the long-term sustainability of this investment pattern and its alignment with SDG 12: Responsible Consumption and Production, due to the immense resources required.
Challenges to Sustainable and Inclusive Development
The technology-driven growth model presents several challenges to achieving holistic sustainable development, particularly concerning energy, economic inclusivity, and employment.
- Economic Diversification and Inclusivity (SDG 8): The sluggish performance of other economic sectors, including manufacturing, real estate, and retail, indicates that the benefits of this growth are not being widely distributed. The slowdown in overall job creation, contrasted with high GDP figures, points to a disconnect between headline growth and the creation of decent work for all.
- Energy Consumption (SDG 7): The explosive growth in data centers, which are highly energy-intensive, poses a significant challenge to SDG 7: Affordable and Clean Energy. The analysis suggests that absent the AI boom, electricity prices could be lower, highlighting the strain this infrastructure places on energy resources and the critical need to power this expansion with renewable sources to ensure sustainability.
- Sustainable Production Patterns (SDG 12): The rapid, large-scale construction of data centers necessitates a massive consumption of materials and electronic components. This raises critical questions about resource efficiency, electronic waste management, and the overall sustainability of the production cycle, central tenets of SDG 12.
Concluding Assessment
The U.S. economy in the first half of 2025 presents a paradox of strong statistical growth fueled by a narrow, resource-intensive sector. While investment in digital infrastructure strongly aligns with the innovation and infrastructure goals of SDG 9, it simultaneously creates significant hurdles for achieving the inclusive and sustainable economic growth outlined in SDG 8 and the clean energy targets of SDG 7. The long-term viability of this economic model is contingent upon mitigating its environmental impact and ensuring its economic benefits are distributed more equitably across all sectors of society.
Analysis of Sustainable Development Goals in the Article
1. Which SDGs are addressed or connected to the issues highlighted in the article?
-
SDG 8: Decent Work and Economic Growth
The article is fundamentally about economic growth, specifically the Gross Domestic Product (GDP) of the United States. It analyzes the drivers of this growth, discusses the overall health of the economy, and questions the sustainability of growth that is heavily concentrated in one sector. The entire discussion revolves around macroeconomic performance, which is the core of SDG 8.
-
SDG 9: Industry, Innovation and Infrastructure
The article directly links economic growth to massive investments in a specific type of infrastructure: data centers. It highlights the role of innovation, particularly in artificial intelligence and information processing technology, as the primary engine of the economy. The text details the “buildout” of “high-tech infrastructure” by major technology companies, which aligns perfectly with the themes of industry, innovation, and infrastructure in SDG 9.
2. What specific targets under those SDGs can be identified based on the article’s content?
-
SDG 8: Decent Work and Economic Growth
-
Target 8.1: Sustain per capita economic growth.
The article is centered on measuring and understanding U.S. GDP growth. It provides specific figures, such as the calculation that without technology investment, “GDP growth would have been just 0.1% on an annualized basis.” This directly relates to the goal of sustaining economic growth.
-
Target 8.2: Achieve higher levels of economic productivity through diversification, technological upgrading and innovation.
The article explicitly identifies “technological upgrading and innovation” as the key driver of economic growth. The “remarkable surge in data-center infrastructure” and investment in “information-processing equipment and software” are presented as the primary sources of economic productivity, accounting for “fully 92% of GDP growth” in the first half of 2025.
-
Target 8.1: Sustain per capita economic growth.
-
SDG 9: Industry, Innovation and Infrastructure
-
Target 9.1: Develop quality, reliable, sustainable and resilient infrastructure… to support economic development.
The article focuses on the development of “high-tech infrastructure” (data centers) and its pivotal role in “shaping macroeconomic outcomes” and supporting economic development. While the text doesn’t discuss sustainability or resilience, it clearly identifies this infrastructure buildout as a critical component of the national economy.
-
Target 9.5: Enhance scientific research, upgrade the technological capabilities of industrial sectors… including… private research and development spending.
The article provides concrete examples of massive private spending to upgrade technological capabilities. It notes that tech giants have “poured tens of billions of dollars into building and upgrading data centers” and that “hyperscaler capex on data center and related items has risen fourfold and is nearing $400 billion annually.” This directly reflects the investment in research, development, and technological enhancement central to this target.
-
Target 9.1: Develop quality, reliable, sustainable and resilient infrastructure… to support economic development.
3. Are there any indicators mentioned or implied in the article that can be used to measure progress towards the identified targets?
-
Indicator for Target 8.1 (related to official indicator 8.1.1: Annual growth rate of real GDP per capita):
The article provides several data points that function as direct measures of GDP growth.
- Excluding technology, “GDP growth would have been just 0.1% on an annualized basis.”
- Investment in information-processing equipment and software “accounted for fully 92% of GDP growth over that period.”
- “It’s estimated that data center-linked spending is adding roughly 100 basis points to U.S. real GDP growth.”
-
Indicator for Target 9.5 (related to official indicator 9.5.1: Research and development expenditure as a proportion of GDP):
The article provides specific monetary values and proportions for investment in technology and infrastructure, which serve as indicators of R&D and innovation spending.
- “Investment in information-processing equipment and software was only 4% of U.S. GDP for the first half of 2025.”
- “Hyperscaler capex on data center and related items has risen fourfold and is nearing $400 billion annually.”
- “The top 10 spenders accounting for nearly a third of all spending.”
4. Summary Table of SDGs, Targets, and Indicators
| SDGs | Targets | Indicators |
|---|---|---|
| SDG 8: Decent Work and Economic Growth |
|
|
| SDG 9: Industry, Innovation and Infrastructure |
|
|
Source: fortune.com

What is Your Reaction?
 Like
0
Like
0
 Dislike
0
Dislike
0
 Love
0
Love
0
 Funny
0
Funny
0
 Angry
0
Angry
0
 Sad
0
Sad
0
 Wow
0
Wow
0