Aquaculture Therapeutics Market Growth Analysis | CAGR of 8.5% – Market.us Media
Report on the Global Aquaculture Therapeutics Market: An Analysis of Growth and Alignment with Sustainable Development Goals
Executive Summary
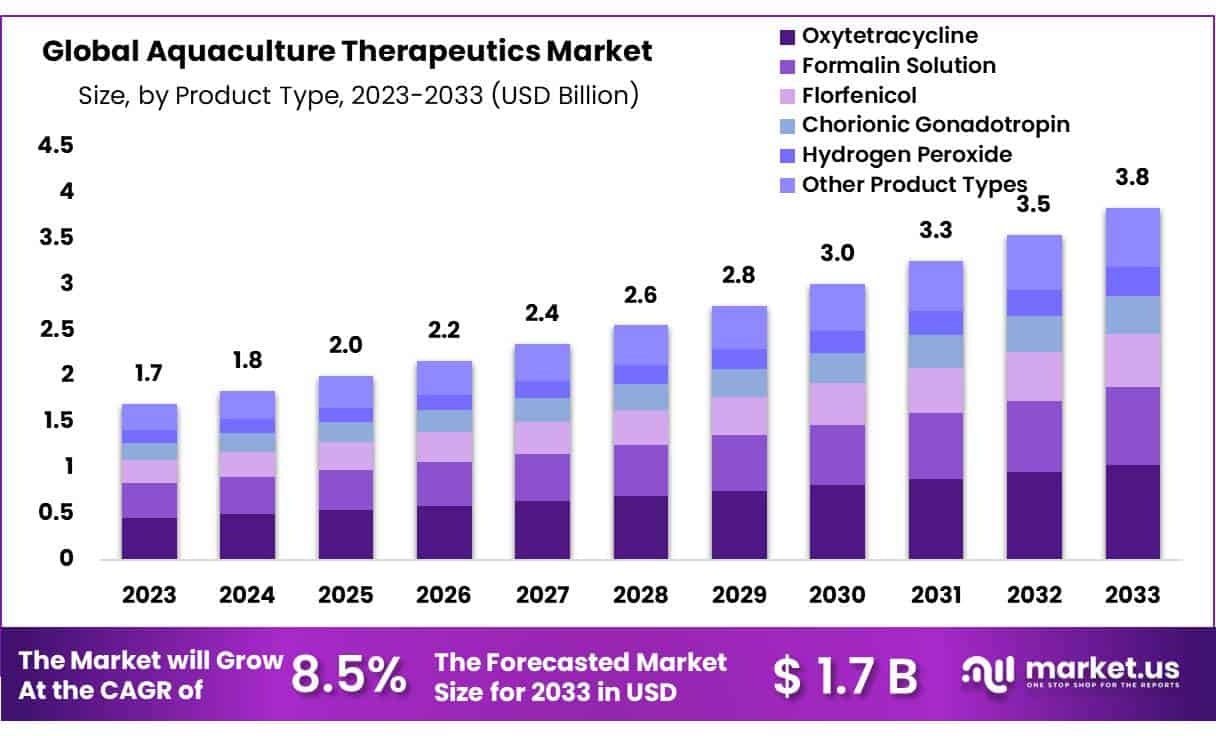
The global aquaculture therapeutics market is projected to experience substantial growth, expanding from USD 1.8 billion in 2024 to an estimated USD 3.8 billion by 2033, at a Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 8.5%. This expansion is fundamentally linked to the global imperative for sustainable food production and the achievement of several United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). The increasing demand for seafood as a primary protein source necessitates advanced health management in aquaculture to ensure food security (SDG 2: Zero Hunger), promote responsible production (SDG 12: Responsible Consumption and Production), and protect aquatic ecosystems (SDG 14: Life Below Water).
Market Dynamics and Contribution to Sustainable Development
Primary Market Drivers and SDG Linkages
The market’s growth is propelled by factors that directly support global sustainability targets:
- Global Food Security (SDG 2): Rising global demand for seafood requires increased aquaculture productivity. Therapeutics are essential for preventing disease-related losses, thereby ensuring a stable and healthy supply of aquatic protein.
- Economic Viability (SDG 8): Disease outbreaks cause significant economic losses for aquaculture producers. Effective therapeutics protect livelihoods and support economic growth in coastal and rural communities dependent on aquaculture.
- Aquatic Health and Ecosystem Protection (SDG 14): The need to manage bacterial, viral, and parasitic infections in farmed species is critical for maintaining both farm productivity and the health of surrounding aquatic environments.
Emerging Trends in Sustainable Aquaculture
A significant shift towards sustainability is reshaping the market, with key trends directly contributing to global health and environmental goals.
- Transition from Antibiotics to Preventative Care (SDG 3): In response to the global threat of antimicrobial resistance (AMR), the industry is moving away from traditional antibiotics like Oxytetracycline (currently 27% of the market) towards preventative solutions such as vaccines, probiotics, and immunostimulants. This trend is crucial for achieving SDG 3 (Good Health and Well-being) by reducing the development of drug-resistant pathogens.
- Adoption of Eco-Friendly Therapeutics (SDG 12 & SDG 14): There is a growing emphasis on natural and biodegradable treatments that minimize environmental impact. This focus on responsible production practices supports the conservation of marine ecosystems and aligns with SDG 12 and SDG 14.
- Integrated Health and Water Quality Management: Advanced water treatment technologies and integrated health programs are being implemented to create healthier, more resilient aquaculture systems. This holistic approach prevents disease outbreaks and reduces the need for chemical interventions, promoting sustainable use of water resources.
Regional Analysis and Global Goal Contributions
North America
North America is projected to hold a 35% market share, driven by advanced aquaculture infrastructure and stringent regulatory frameworks. The region’s focus on technological innovation and compliance with high safety standards sets a benchmark for responsible production (SDG 12) and contributes to the development of sustainable aquaculture models globally.
Asia-Pacific
The Asia-Pacific region is expected to exhibit the highest growth rate due to its massive aquaculture output. The increasing adoption of effective therapeutics in this region is critical for securing global food supply chains (SDG 2) and improving the sustainability of an industry that is vital to the economies of many developing nations (SDG 8).
Strategic Implications for the 2030 Agenda
The evolution of the aquaculture therapeutics market has direct implications for the achievement of the Sustainable Development Goals.
- Disease Prevention and Food Safety: The use of vaccines and advanced biologics enhances fish welfare, improves food safety, and ensures a consistent supply of nutritious food, directly supporting SDG 2.
- Combating Antimicrobial Resistance: By prioritizing non-antibiotic treatments, the market plays a vital role in the global effort to combat AMR, a key public health target under SDG 3.
- Sustainable Production Systems: The development of environmentally responsible disease control strategies and adherence to Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) are foundational to building sustainable food systems as envisioned in SDG 12.
- Protecting Marine Biodiversity: Effective and targeted therapeutics help prevent the transmission of diseases from farmed to wild populations, thereby protecting marine biodiversity and contributing to the goals of SDG 14.
Conclusion
The global aquaculture therapeutics market is on a positive growth trajectory, driven by the dual needs of ensuring global food security and promoting environmental sustainability. The industry’s strategic shift towards preventative care, biotechnology, and eco-friendly solutions demonstrates a strong alignment with the UN Sustainable Development Goals. Future market expansion will be contingent on continued innovation in therapeutics that enhance productivity while safeguarding public health and aquatic ecosystems, positioning the sector as a key contributor to a sustainable global future.
Analysis of Sustainable Development Goals in the Article
1. Which SDGs are addressed or connected to the issues highlighted in the article?
- SDG 2: Zero Hunger
- The article focuses on aquaculture, a critical component of global food production. It highlights the “rising demand for sustainable seafood production” and the “growth of fish consumption globally, driven by consumer preference for high-protein diets,” which directly relates to achieving food security and improved nutrition.
- SDG 3: Good Health and Well-being
- The article discusses the management of aquatic animal health to prevent “bacterial and viral infections.” A key trend mentioned is the “Reduction in Antibiotic Use” to limit antimicrobial resistance, which is a significant global health risk. This, along with ensuring “food safety,” connects aquaculture practices to human health outcomes.
- SDG 8: Decent Work and Economic Growth
- The article details the economic aspects of the aquaculture industry, including its market size (projected to reach USD 3.8 billion) and growth rate (8.5% CAGR). It also notes that disease outbreaks cause “economic losses faced by aquaculture producers,” and that therapeutics enhance “operational profitability,” linking sustainable practices to economic productivity and growth.
- SDG 9: Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure
- The text emphasizes “innovation in biologics,” “advancements in water treatment technologies,” and the “introduction of next-generation vaccines.” It also points to “investment in aquaculture biotechnology” and “research collaborations” as key drivers, aligning with the goal of fostering innovation and upgrading industrial technological capabilities.
- SDG 12: Responsible Consumption and Production
- The article repeatedly mentions the shift towards sustainability. Phrases like “sustainable aquaculture practices,” “natural and eco-friendly therapeutic solutions,” and “environmentally responsible disease control strategies” show a clear connection to promoting sustainable production patterns within the aquaculture industry.
- SDG 14: Life Below Water
- The entire article is centered on aquaculture, which directly impacts aquatic ecosystems. It highlights the importance of promoting “healthier and more resilient aquaculture ecosystems” and mitigating “environmental risks” through “environmentally responsible therapeutics.” This directly addresses the need to conserve and sustainably use marine resources.
- SDG 17: Partnerships for the Goals
- The article mentions that “Strategic partnerships, research collaborations, and increasing investment” are expected to create significant opportunities. This points to the importance of collaboration between industry participants, researchers, and governments to achieve sustainable development in the sector.
2. What specific targets under those SDGs can be identified based on the article’s content?
-
SDG 2: Zero Hunger
- Target 2.4: By 2030, ensure sustainable food production systems and implement resilient agricultural practices that increase productivity and production. The article’s focus on “sustainable seafood production,” “enhanced productivity,” and creating “resilient aquaculture ecosystems” directly supports this target.
-
SDG 3: Good Health and Well-being
- Target 3.d: Strengthen the capacity of all countries, in particular developing countries, for early warning, risk reduction and management of national and global health risks. The trend of “Reduction in Antibiotic Use” to “limit antimicrobial resistance” is a direct action towards managing a major global health risk.
-
SDG 9: Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure
- Target 9.5: Enhance scientific research, upgrade the technological capabilities of industrial sectors in all countries…encouraging innovation. The article’s emphasis on “investment in aquaculture biotechnology,” “research collaborations,” and the development of “next-generation vaccines” aligns with this target.
-
SDG 12: Responsible Consumption and Production
- Target 12.2: By 2030, achieve the sustainable management and efficient use of natural resources. The industry’s transition toward “natural and eco-friendly therapeutic solutions” and “responsible aquaculture practices” reflects efforts to manage resources sustainably.
-
SDG 14: Life Below Water
- Target 14.2: By 2020, sustainably manage and protect marine and coastal ecosystems to avoid significant adverse impacts. The article’s focus on promoting “healthier and more resilient aquaculture ecosystems” and using “environmentally responsible disease control strategies” contributes to this goal.
-
SDG 17: Partnerships for the Goals
- Target 17.6: Enhance North-South, South-South and triangular regional and international cooperation on and access to science, technology and innovation. The mention of “Strategic partnerships” and “research collaborations” as drivers of opportunity reflects the spirit of this target.
3. Are there any indicators mentioned or implied in the article that can be used to measure progress towards the identified targets?
-
For Target 2.4 (Sustainable Food Production)
- Implied Indicator: Growth in sustainable aquaculture output. The article provides market size projections (“USD 3.8 Billion by 2033”) for therapeutics that support “sustainable seafood production,” which can serve as a proxy for the growth of sustainable practices.
-
For Target 3.d (Managing Global Health Risks)
- Implied Indicator: Rate of adoption of alternatives to antibiotics. The article highlights a key trend of “Reduction in Antibiotic Use” and a shift towards “vaccines, better farm hygiene, and alternative biological treatments,” which can be measured to track progress.
-
For Target 9.5 (Enhance Research and Innovation)
- Implied Indicator: Investment in aquaculture R&D and biotechnology. The article states that “increasing investment in aquaculture biotechnology” is a key factor, suggesting that tracking this investment would be a relevant measure of progress.
-
For Target 12.2 (Sustainable Management of Natural Resources)
- Implied Indicator: Market share of eco-friendly products. The article notes a “clear transition toward natural and eco-friendly therapeutic solutions.” Measuring the market share growth of these products versus traditional ones would indicate progress.
-
For Target 14.2 (Protect Marine Ecosystems)
- Implied Indicator: Adoption of environmentally responsible practices. The implementation of “integrated fish health programs” and “environmentally responsible disease control strategies” can be monitored to assess the industry’s efforts to protect aquatic ecosystems.
Summary of SDGs, Targets, and Indicators
| SDGs | Targets | Indicators |
|---|---|---|
| SDG 2: Zero Hunger | Target 2.4: Ensure sustainable food production systems and implement resilient agricultural practices. | Growth in market size for therapeutics supporting “sustainable seafood production” (e.g., projected market value of USD 3.8 billion). |
| SDG 3: Good Health and Well-being | Target 3.d: Strengthen capacity for management of national and global health risks. | Adoption rate of alternatives to antibiotics, such as vaccines and biologics, to limit antimicrobial resistance. |
| SDG 9: Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure | Target 9.5: Enhance scientific research and upgrade technological capabilities. | Level of “investment in aquaculture biotechnology” and development of “next-generation vaccines.” |
| SDG 12: Responsible Consumption and Production | Target 12.2: Achieve the sustainable management and efficient use of natural resources. | Market share and adoption rate of “natural and eco-friendly therapeutic solutions.” |
| SDG 14: Life Below Water | Target 14.2: Sustainably manage and protect marine and coastal ecosystems. | Implementation of “integrated fish health programs” and “environmentally responsible disease control strategies.” |
| SDG 17: Partnerships for the Goals | Target 17.6: Enhance cooperation on and access to science, technology and innovation. | Number of “Strategic partnerships” and “research collaborations” within the aquaculture industry. |
Source: media.market.us
What is Your Reaction?
 Like
0
Like
0
 Dislike
0
Dislike
0
 Love
0
Love
0
 Funny
0
Funny
0
 Angry
0
Angry
0
 Sad
0
Sad
0
 Wow
0
Wow
0












































































