EV Battery Testing Market Size, Share | CAGR of 18.5% – Market.us
Global Electric Vehicle Battery Testing Market: A Report on Sustainable Development and Innovation
Executive Summary
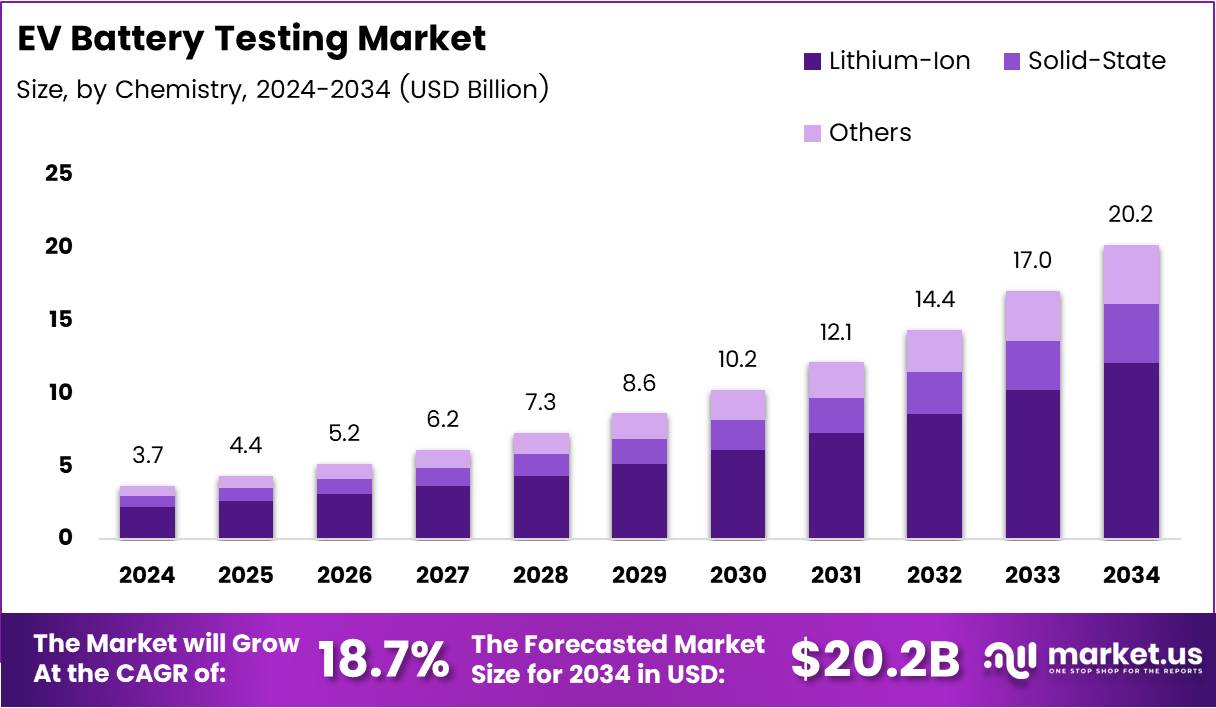
The Global Electric Vehicle (EV) Battery Testing Market is undergoing significant expansion, with a projected value of USD 20.2 Billion by 2034, increasing from USD 3.7 Billion in 2024 at a Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 18.7%. This growth is intrinsically linked to the global pursuit of the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), particularly SDG 7 (Affordable and Clean Energy), SDG 11 (Sustainable Cities and Communities), and SDG 13 (Climate Action). The market provides essential validation services for EV batteries, ensuring their safety, reliability, and performance, which are foundational for the worldwide transition to sustainable transportation. By guaranteeing the integrity of clean energy technologies, the EV battery testing sector directly supports the development of resilient infrastructure (SDG 9) and promotes responsible production patterns (SDG 12).
Key Market Insights and Alignment with SDGs
- Market Growth: The market is forecast to reach USD 20.2 Billion by 2034, reflecting the escalating global commitment to climate action (SDG 13) through vehicle electrification.
- Dominant Chemistry: Lithium-Ion batteries command a 72.5% market share, highlighting their critical role in the current phase of the clean energy transition (SDG 7).
- Leading Form Factor: Prismatic batteries lead with a 42.1% share, with their packaging efficiency contributing to more resource-effective vehicle designs (SDG 12).
- Propulsion Share: Battery Electric Vehicles (BEVs) represent 56.6% of the market, underscoring a decisive shift towards zero-emission transport to create sustainable cities (SDG 11).
- Battery Technology: Cell-To-Pack technology holds a 44.8% share, an innovation that enhances energy density and supports the industry’s goal of building more efficient and sustainable infrastructure (SDG 9).
- Vehicle Type: Light-Duty Vehicles dominate with an 82.3% share, indicating that mass consumer adoption is a primary driver for reducing the carbon footprint of personal transport.
- Regional Leadership: The Asia Pacific region leads with a 45.9% market share, valued at USD 1.6 Billion, positioning it as a key player in global sustainable production and climate action efforts.
Market Segmentation Analysis
Analysis by Chemistry
The Lithium-Ion segment, with a 72.5% share, remains central to achieving affordable and clean energy (SDG 7). Rigorous testing ensures the safety and longevity of this established technology. Concurrently, the development of Solid-State batteries represents a significant innovation (SDG 9), with testing focused on validating their potential for enhanced safety and energy density, further advancing sustainable energy storage. Testing of other chemistries supports diversification and the search for more sustainable materials, aligning with principles of responsible consumption and production (SDG 12).
Analysis by Form
Prismatic cells dominate with a 42.1% share, as their structural design allows for efficient use of space and materials, a key aspect of responsible production (SDG 12). Testing of Pouch cells supports the development of lightweight, energy-dense solutions that improve vehicle efficiency and reduce material consumption. The continued relevance of Cylindrical cells in performance applications necessitates standardized testing to ensure safety and reliability, contributing to the overall resilience of EV technology.
Analysis by Propulsion
Battery Electric Vehicles (BEVs) hold a 56.6% share, directly contributing to the goals of reducing urban pollution (SDG 11) and combating climate change (SDG 13). The testing of batteries for Hybrid (HEV) and Plug-In Hybrid (PHEV) vehicles supports transitional pathways for regions gradually adopting cleaner technologies. Testing for Fuel Cell Electric Vehicles (FCEVs) focuses on auxiliary systems, fostering innovation in diverse clean energy solutions (SDG 7).
Analysis by Battery Technology
Cell-To-Pack technology leads with a 44.8% share. This design simplifies manufacturing and enhances energy density, representing an industrial innovation (SDG 9) that makes EVs more efficient and accessible. Testing of Cell-To-Module and Cell-To-Chassis configurations ensures that these advanced, integrated designs meet stringent safety standards, which is crucial for building trust in sustainable transportation infrastructure.
Analysis by EV Type
Light-Duty Vehicles account for 82.3% of the market, signifying that the decarbonization of personal transport is a major contributor to climate action (SDG 13). The growing need for testing batteries in Heavy Commercial Vehicles reflects the expansion of electrification into logistics and public transport, which is vital for creating sustainable cities and communities (SDG 11) by reducing emissions from commercial fleets.
Key Market Segments
-
By Chemistry
- Lithium-Ion
- Solid-State
- Others
-
By Form
- Prismatic
- Pouch
- Cylindrical
-
By Propulsion
- Battery Electric Vehicle
- Hybrid Electric Vehicle
- Plug-In Hybrid Electric Vehicle
- Fuel Cell Electric Vehicle
-
By Battery Technology
- Cell-To-Pack
- Cell-To-Module
- Cell-To-Chassis/Cell-To-Body
-
By EV Type
- Light-Duty Vehicle
- Heavy Commercial Vehicle
Market Dynamics: Drivers, Restraints, and Opportunities
Drivers
The primary driver is the accelerating global adoption of EVs, a critical strategy for achieving climate action targets (SDG 13). Strict government regulations on battery safety and performance mandate comprehensive testing, fostering the development of resilient and sustainable infrastructure (SDG 9). Continuous innovation in battery chemistries necessitates rigorous validation to ensure these new technologies are safe and effective, further propelling industry innovation.
Restraints
The high capital investment required for advanced testing equipment can be a barrier, potentially limiting participation from smaller enterprises and emerging economies. Furthermore, a lack of globally harmonized testing standards complicates compliance and can slow the deployment of clean energy technologies, highlighting a need for greater international cooperation (SDG 17).
Growth Factors
Significant opportunities arise from the development of next-generation technologies like solid-state batteries, which require new testing protocols and drive innovation (SDG 9). The growing emphasis on the circular economy, including battery second-life applications and recycling, creates demand for testing solutions that support responsible consumption and production (SDG 12).
Emerging Trends
The adoption of digital twin models and real-time monitoring represents a shift towards more efficient and less resource-intensive testing methods, aligning with SDG 12. Increased focus on fast-charging compatibility is crucial for building user-friendly infrastructure (SDG 9) that encourages wider EV adoption. The development of modular and automated test platforms enhances production efficiency, supporting the industry’s capacity to scale up and meet global climate goals.
Regional Analysis and SDG Contributions
Asia Pacific
Holding a 45.9% market share, the Asia Pacific region is central to the global supply chain for EVs and batteries. Its manufacturing scale is vital for making clean energy technologies accessible worldwide (SDG 7). The region’s leadership carries a significant responsibility to advance sustainable production practices (SDG 12) and contribute to global climate action (SDG 13).
North America
The North American market is driven by strong federal incentives and regulatory focus on safety and sustainability. Investments in domestic manufacturing and R&D contribute to building resilient infrastructure (SDG 9) and advancing clean energy innovation.
Europe
Europe’s market is characterized by stringent emissions standards and ambitious electrification targets. A strong focus on the circular economy and sustainable battery production drives demand for comprehensive lifecycle testing, directly supporting SDG 12.
Middle East & Africa
This emerging region is beginning to invest in clean mobility infrastructure. Growth in this market presents an opportunity to build sustainable transport systems that align with SDG 9 and SDG 11 from the outset.
Latin America
Latin America shows steady growth as awareness of sustainable transportation increases. The development of regulatory frameworks for EVs will be crucial for the region’s contribution to global climate goals and the creation of sustainable cities.
Key Company Developments
Leading companies in the EV battery testing market are expanding their capabilities to support the global transition to sustainable energy. Their investments in advanced laboratories, acquisitions of specialized firms, and development of innovative testing solutions are essential for building the industrial capacity (SDG 9) required to meet rising demand and ensure the safety and reliability of EV technology. Recent developments include:
- UL Solutions launched its Europe Advanced Battery Laboratory in Germany (May 2025) to expand advanced testing and certification, strengthening the infrastructure for clean technology.
- Unico LLC acquired Present Power Systems (January 2024) to broaden its portfolio, integrating solutions that span the electrification value chain from testing to charging.
- TÜV SÜD consolidated its ownership of its battery testing subsidiary (November 2024) to accelerate strategic development in support of safe and reliable battery technology.
- AVL was commissioned by Volkswagen’s PowerCo SE (November 2024) to equip a new battery-cell testing laboratory, a key project for advancing battery innovation and quality assurance.
Analysis of Sustainable Development Goals in the Article
1. Which SDGs are addressed or connected to the issues highlighted in the article?
The article on the Global EV Battery Testing Market connects to several Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) by highlighting the technological, industrial, and economic shifts towards electric mobility, which is a key strategy for sustainable development. The following SDGs are addressed:
- SDG 7: Affordable and Clean Energy: The transition to Electric Vehicles (EVs) is central to increasing the use of clean energy in the transport sector. The article’s focus on improving battery performance, safety, and efficiency directly supports the broader adoption of EVs, which rely on electricity—a progressively cleaner energy source.
- SDG 9: Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure: The article is fundamentally about the industry, innovation, and infrastructure supporting the EV revolution. It details the growth of a specialized market (EV battery testing), advancements in battery technologies (“solid-state,” “next-generation chemistries”), and the development of supporting infrastructure (“gigafactories,” “advanced testing equipment”).
- SDG 11: Sustainable Cities and Communities: Although not explicitly stated, the large-scale adoption of EVs, which the article describes as “accelerating,” is a critical component for creating sustainable cities. EVs help reduce urban air and noise pollution, contributing to healthier and more sustainable urban environments.
- SDG 12: Responsible Consumption and Production: The article touches upon sustainability beyond just vehicle emissions. It mentions a growing interest in “battery lifecycle assessment, recycling evaluation, and second-life repurposing,” which are key elements of establishing circular economies and promoting responsible production patterns for batteries.
- SDG 13: Climate Action: The global shift to EVs is one of the most significant actions being taken to mitigate climate change by reducing greenhouse gas emissions from the transportation sector. The article underscores this by referencing “strong government policies promoting clean mobility” and “stringent emission regulations” that drive the EV market forward.
2. What specific targets under those SDGs can be identified based on the article’s content?
Based on the article’s content, several specific SDG targets can be identified:
- Target 7.3: By 2030, double the global rate of improvement in energy efficiency.
- Explanation: The article discusses the industry’s pursuit of “extended range and efficiency” and the development of “lightweight battery designs” and “Cell-To-Pack” technology, which offers “enhanced energy density.” These innovations are aimed at improving the energy efficiency of EVs, directly contributing to this target.
- Target 9.4: By 2030, upgrade infrastructure and retrofit industries to make them sustainable, with increased resource-use efficiency and greater adoption of clean and environmentally sound technologies and industrial processes.
- Explanation: The entire EV battery testing market represents an upgrade of industrial processes to support a clean technology. The article highlights “advancements in battery chemistries,” “AI-driven predictive analytics,” and “digital twin testing models” as innovations that make the industry more efficient and sustainable.
- Target 9.5: Enhance scientific research, upgrade the technological capabilities of industrial sectors in all countries.
- Explanation: The article details significant R&D efforts, noting that “continuous advancements in battery chemistries—such as high-energy-density cells and new anode materials—further strengthen the need for rigorous testing.” The emergence of testing for “solid-state and next-generation battery technologies” is a direct reflection of enhancing scientific research and technological capabilities.
- Target 11.6: By 2030, reduce the adverse per capita environmental impact of cities, including by paying special attention to air quality.
- Explanation: The article’s central theme is the growth of the EV market, which is a primary strategy for improving urban air quality. The statistic that “electric car sales reached 17 million in 2024, representing over 20% of global new-car sales” indicates a significant move towards reducing the environmental impact of transportation in cities.
- Target 12.5: By 2030, substantially reduce waste generation through prevention, reduction, recycling and reuse.
- Explanation: The article explicitly mentions that the market is “benefiting from growing interest in battery lifecycle assessment, recycling evaluation, and second-life repurposing.” This points directly to industry efforts to manage battery waste and create a “circular battery ecosystem,” aligning with the goal of waste reduction and reuse.
- Target 13.2: Integrate climate change measures into national policies, strategies and planning.
- Explanation: The article identifies government action as a key driver for the market, mentioning “ongoing government investments and evolving regulations,” “incentive-driven EV manufacturing programs,” and “stringent emission regulations.” These are all examples of climate change measures being integrated into national policies.
3. Are there any indicators mentioned or implied in the article that can be used to measure progress towards the identified targets?
Yes, the article contains several quantitative and qualitative indicators that can be used to measure progress:
- Rate of EV Adoption: The article states that “electric car sales reached 17 million in 2024, representing over 20% of global new-car sales and expanding the fleet to almost 58 million vehicles, more than 3× the 2021 level.” This is a direct indicator of the adoption of clean technology (Target 9.4) and progress in reducing transport emissions (Target 11.6, 13.2).
- Market Growth in Supporting Infrastructure: The projection that the “Global EV Battery Testing Market size is expected to be worth around USD 20.2 Billion by 2034, from USD 3.7 Billion in 2024” serves as an indicator of the level of investment in the infrastructure required to ensure the safety and reliability of clean energy technologies (Target 9.4).
- Growth in Battery Production and Demand: The statistic that “global lithium-ion battery demand rose 65% in 2022, climbing from 330 GWh in 2021 to 550 GWh in 2022” indicates the scale of industrial transition towards electrification (Target 9.4).
- Investment in R&D and Innovation: The article’s discussion of “accelerated testing” for “Solid-State technology” and the use of “AI-driven predictive analytics” and “digital twin models” implies a high level of investment and activity in research and development, which is a key indicator for progress on Target 9.5.
- Implementation of Government Policies: The mention of “strong government policies promoting clean mobility,” “new safety mandates,” and “stringent emission regulations” are qualitative indicators that measure the integration of climate action into national planning (Target 13.2).
- Development of Circular Economy Practices: The reference to “growing interest in battery lifecycle assessment, recycling evaluation, and second-life repurposing” is a qualitative indicator that shows progress towards establishing systems for responsible production and waste reduction (Target 12.5).
4. Summary Table of SDGs, Targets, and Indicators
| SDGs | Targets | Indicators Identified in the Article |
|---|---|---|
| SDG 7: Affordable and Clean Energy | 7.3: Improve energy efficiency. | Development of technologies for “extended range and efficiency,” “lightweight battery designs,” and “enhanced energy density.” |
| SDG 9: Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure | 9.4: Upgrade infrastructure and industries for sustainability and adopt clean technologies. | Growth of the EV battery testing market from USD 3.7B to USD 20.2B; Growth in battery demand (550 GWh in 2022); Adoption of “AI-driven predictive analytics.” |
| 9.5: Enhance scientific research and upgrade technological capabilities. | Focus on testing for “solid-state and next-generation battery technologies”; Use of “advanced battery simulation tools.” | |
| SDG 11: Sustainable Cities and Communities | 11.6: Reduce the adverse per capita environmental impact of cities (e.g., air quality). | Increase in EV sales to 17 million in 2024, representing over 20% of global new-car sales. |
| SDG 12: Responsible Consumption and Production | 12.5: Substantially reduce waste generation through recycling and reuse. | Growing interest in “battery lifecycle assessment, recycling evaluation, and second-life repurposing” to support “circular battery ecosystems.” |
| SDG 13: Climate Action | 13.2: Integrate climate change measures into national policies and planning. | Mention of “strong government policies promoting clean mobility,” “incentive-driven EV manufacturing programs,” and “stringent emission regulations.” |
Source: market.us
What is Your Reaction?
 Like
0
Like
0
 Dislike
0
Dislike
0
 Love
0
Love
0
 Funny
0
Funny
0
 Angry
0
Angry
0
 Sad
0
Sad
0
 Wow
0
Wow
0























































;Resize=620#)






















