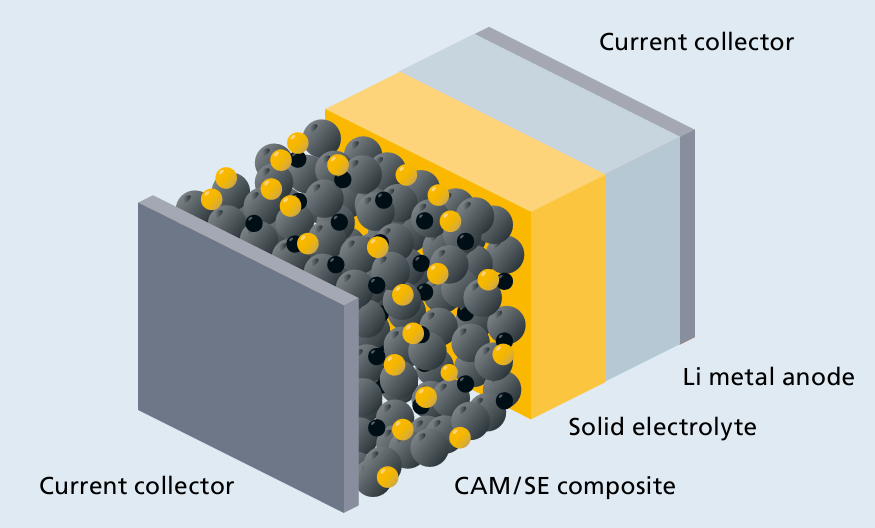
Xcel Energy proposes 200MW distributed battery storage network in Minnesota – Energy-Storage.News

Report on Xcel Energy’s Proposed 200MW Battery Storage Network in Minnesota and Alignment with Sustainable Development Goals
Project Overview
- Proponent: Xcel Energy, a United States-based utility.
- Project Scope: Development of a 200MW distributed battery energy storage system (BESS) network.
- Location: Various sites across the state of Minnesota, US.
- Objective: To enhance grid stability, integrate renewable energy sources, and improve energy resilience for communities, thereby contributing to key sustainability targets.
Contribution to Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs)
The proposed initiative by Xcel Energy demonstrates a significant commitment to advancing several key United Nations Sustainable Development Goals through strategic infrastructure investment.
-
SDG 7: Affordable and Clean Energy
- The battery storage network is critical for increasing the share of renewable energy in the state’s energy mix by storing excess generation from wind and solar sources.
- It ensures a reliable and continuous supply of clean energy, addressing the intermittency of renewables.
- This investment promotes modern and sustainable energy infrastructure, directly supporting Target 7.2 (Increase global percentage of renewable energy) and 7.a (Promote access to research, technology and investments in clean energy).
-
SDG 9: Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure
- The project represents a significant upgrade to regional energy infrastructure, making it more resilient, reliable, and sustainable.
- Deploying a distributed BESS network is an innovative approach to grid management, fostering technological advancement in the energy sector.
- This aligns with Target 9.4, which calls for upgrading infrastructure to make it sustainable with increased resource-use efficiency and greater adoption of clean technologies.
-
SDG 11: Sustainable Cities and Communities
- By enhancing grid stability and preventing power outages, the network contributes to the safety and resilience of urban and rural communities in Minnesota.
- A reliable power supply is fundamental for inclusive, safe, and sustainable community development.
- The initiative supports Target 11.b by contributing to the implementation of integrated policies for resource efficiency and resilience to disasters.
-
SDG 13: Climate Action
- The primary function of the energy storage network is to facilitate a transition away from fossil fuels by enabling greater reliance on renewable energy.
- This directly reduces greenhouse gas emissions from the power sector, contributing to national and global climate change mitigation efforts.
- The project is a tangible action to strengthen resilience and adaptive capacity to climate-related hazards, in line with Target 13.1.
Analysis of Sustainable Development Goals in the Article
-
Which SDGs are addressed or connected to the issues highlighted in the article?
The article on Xcel Energy’s plan to build a 200MW battery storage network in Minnesota connects to several Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). The primary focus on clean energy infrastructure directly aligns with goals concerning energy, infrastructure, climate action, and sustainable communities.
- SDG 7: Affordable and Clean Energy: This is the most directly relevant SDG. The project involves building a battery storage network, which is a critical technology for integrating variable renewable energy sources (like solar and wind) into the power grid, thereby increasing the share of clean energy.
- SDG 9: Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure: The article discusses the construction of new, advanced energy infrastructure. A 200MW distributed battery storage network represents a significant technological innovation and an upgrade to existing energy systems, making them more resilient, sustainable, and efficient.
- SDG 11: Sustainable Cities and Communities: By facilitating a more stable and clean energy supply, this project contributes to making cities and communities more sustainable. A reliable grid powered by renewable energy reduces urban pollution and enhances energy security for residents.
- SDG 13: Climate Action: The fundamental purpose of deploying energy storage at this scale is to support the transition away from fossil fuels to renewable energy. This is a direct action to mitigate climate change by reducing greenhouse gas emissions from the power sector.
-
What specific targets under those SDGs can be identified based on the article’s content?
Based on the project described, several specific SDG targets can be identified:
- Target 7.2: “By 2030, increase substantially the share of renewable energy in the global energy mix.” The 200MW battery storage network is an enabling infrastructure designed to store excess renewable energy and deploy it when needed, which directly supports the integration of a higher percentage of renewables into the grid.
- Target 7.a: “By 2030, enhance international cooperation to facilitate access to clean energy research and technology… and promote investment in energy infrastructure and clean energy technology.” Xcel Energy’s proposal represents a significant investment in clean energy infrastructure and technology (battery storage) at a regional level.
- Target 9.4: “By 2030, upgrade infrastructure and retrofit industries to make them sustainable, with increased resource-use efficiency and greater adoption of clean and environmentally sound technologies…” The battery storage network is a technological upgrade to the energy infrastructure, making it more sustainable by enabling the greater use of clean energy sources.
- Target 13.2: “Integrate climate change measures into national policies, strategies and planning.” This project by a major utility is an example of integrating climate change mitigation measures (promoting renewable energy) into regional energy planning and corporate strategy.
-
Are there any indicators mentioned or implied in the article that can be used to measure progress towards the identified targets?
The article provides a key quantitative indicator that can be used to measure progress:
- Indicator (Directly Mentioned): The capacity of the battery storage network (200MW). This figure is a direct measure of the investment and scale of the new clean energy infrastructure being built. It serves as a tangible metric for progress towards Target 7.a (investment in clean energy infrastructure) and Target 9.4 (adoption of clean technologies).
- Indicator (Implied): Increased share of renewable energy. While the article does not state the resulting percentage increase, the 200MW capacity is a proxy indicator for progress towards Target 7.2. The successful implementation of this project will contribute to an overall increase in the share of renewables in Minnesota’s energy mix, which is the official indicator (Indicator 7.2.1: Renewable energy share in the total final energy consumption).
- Indicator (Implied): Reduction in greenhouse gas emissions. The project’s goal is to facilitate more renewable energy, which displaces fossil fuel generation. Therefore, an implied indicator is the potential reduction in CO2 emissions from the energy sector in Xcel Energy’s service area, which relates to Target 13.2.
-
Create a table with three columns titled ‘SDGs, Targets and Indicators” to present the findings from analyzing the article.
SDGs Targets Indicators SDG 7: Affordable and Clean Energy 7.2: Increase substantially the share of renewable energy in the global energy mix.
7.a: Promote investment in energy infrastructure and clean energy technology.Implied: Increased share of renewable energy in the grid.
Direct: Investment in and deployment of 200MW of battery storage capacity.SDG 9: Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure 9.4: Upgrade infrastructure and retrofit industries to make them sustainable… with greater adoption of clean and environmentally sound technologies. Direct: Construction of a 200MW distributed battery storage network as a clean technology upgrade to energy infrastructure. SDG 11: Sustainable Cities and Communities 11.6: By 2030, reduce the adverse per capita environmental impact of cities. Implied: Reduced air pollution and carbon footprint in Minnesota’s communities due to a cleaner energy grid. SDG 13: Climate Action 13.2: Integrate climate change measures into national policies, strategies and planning. Implied: The proposal by a utility to build the network serves as an indicator of climate action being integrated into corporate and regional energy planning.
Source: energy-storage.news

What is Your Reaction?
 Like
0
Like
0
 Dislike
0
Dislike
0
 Love
0
Love
0
 Funny
0
Funny
0
 Angry
0
Angry
0
 Sad
0
Sad
0
 Wow
0
Wow
0





















































;Resize=620#)