Polymer Mixing Unit Market | Global Market Analysis Report – 2035 – Future Market Insights
Polymer Mixing Unit Market: A Report on Growth, Drivers, and Alignment with Sustainable Development Goals (2025-2035)
Executive Summary: Market Projections and Sustainability Impact
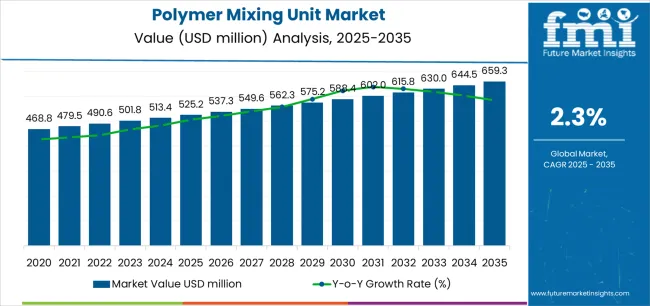
The global polymer mixing unit market is forecast to expand from USD 525.2 million in 2025 to approximately USD 659.3 million by 2035. This growth is intrinsically linked to the global pursuit of the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), particularly SDG 6 (Clean Water and Sanitation). The increasing demand for efficient water and wastewater treatment technologies is a primary market driver, as nations invest in infrastructure to ensure universal access to clean water and manage sanitation safely. Polymer mixing units are critical components in achieving SDG 6.3, which aims to improve water quality by reducing pollution and halving the proportion of untreated wastewater.
Market expansion is further propelled by investments in municipal and industrial infrastructure, which supports SDG 9 (Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure) and SDG 11 (Sustainable Cities and Communities). Stricter environmental regulations on effluent discharge compel industries to adopt advanced systems, promoting SDG 12 (Responsible Consumption and Production) by minimizing chemical waste and enhancing resource efficiency. The trend toward automation and energy-efficient systems also aligns with SDG 7 (Affordable and Clean Energy) and SDG 9, reducing operational costs and environmental footprints in critical sectors like power generation, food processing, and petrochemicals.
Market Performance Indicators (2025-2035)
Market Valuation and Growth
- Market Value (2025): USD 525.2 million
- Market Forecast Value (2035): USD 659.3 million
- Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR): 2.3%
Leading Market Segments (2025)
- By Material Form: Liquid (57.3%)
- By Application: Wastewater Treatment (44.6%)
Key Growth Regions
- Asia Pacific
- North America
- Europe
Core Market Drivers and Their Contribution to Global Goals
Infrastructure, Regulation, and SDG Alignment
- Water Infrastructure Investment: Global investments in water and wastewater facilities, driven by urbanization and the need to replace aging systems, directly support the achievement of SDG 6 and the development of resilient urban environments under SDG 11.
- Regulatory Compliance: Stringent regulations on water quality and effluent discharge are essential policy tools for enforcing SDG 6.3. These mandates drive the adoption of precise polymer dosing systems to protect public health and aquatic ecosystems, contributing to SDG 14 (Life Below Water).
- Emerging Market Urbanization: Rapid urbanization necessitates new treatment capacity, making polymer mixing units essential for effective solids separation and sanitation management, a cornerstone of SDG 11.
Operational Efficiency and Responsible Production
- Chemical Cost Optimization: A focus on reducing chemical consumption aligns with SDG 12 by minimizing waste and promoting resource efficiency. Precise polymer preparation is key to achieving this goal.
- Process Automation: The adoption of automated systems enhances industrial processes and infrastructure, a key target of SDG 9, while reducing manual labor and improving process consistency.
Technology, Sustainability, and Innovation
- Advanced Control Integration: The development of smart, automated mixing units with remote monitoring capabilities represents an advancement in industrial innovation, directly supporting SDG 9.
- Energy Efficiency: The growing demand for energy-efficient mixing technologies contributes to SDG 7 and SDG 12 by reducing the energy intensity of water treatment operations.
- Sustainable Water Management: An industrial focus on water reuse and zero liquid discharge principles is a direct application of circular economy models, advancing both SDG 6 and SDG 12.
Market Segmentation Analysis
Analysis by Material Form
- Liquid Polymer Systems: Holding a 57.3% market share in 2025, these systems offer operational simplicity and enhanced safety by eliminating dust, which contributes to better occupational health outcomes (SDG 3: Good Health and Well-being). Their suitability for smaller facilities aids in the decentralization of water treatment, expanding access in line with SDG 6.
- Powder Polymer Systems: Accounting for 42.7% of the market, powder formulations provide significant cost advantages for large-scale municipal and industrial applications. This economic viability is crucial for financing the large infrastructure projects needed to achieve SDG 6 and SDG 11. Their concentrated form also reduces transportation weight, contributing modestly to lower emissions (SDG 13: Climate Action).
Analysis by Application
- Wastewater Treatment: As the dominant segment (44.6%), this application is the most direct contributor to SDG 6.3. Effective biosolids dewatering, a key function, is essential for sustainable sludge management and creating healthier cities as outlined in SDG 11.
- Paper Industry: This segment supports SDG 12 by enabling greater water recycling and resource efficiency in a water-intensive industry. It helps the sector reduce its environmental footprint and move towards more sustainable production models.
- Chemical Industry: The use of polymer mixing units in this sector is critical for managing industrial effluent and reducing freshwater consumption, aligning with the goals of responsible industrialization (SDG 9) and sustainable production (SDG 12).
- Others: Applications in mining, oil and gas, and food processing are vital for mitigating the environmental impacts of these industries, ensuring they manage water resources responsibly in line with SDG 6 and SDG 12.
Regional Market Analysis and Progress on SDGs
Asia Pacific
Commanding a 38.7% market share, the Asia Pacific region’s growth is driven by substantial infrastructure investments in countries like China and India. These efforts are fundamental to achieving national targets for SDG 6 (Clean Water and Sanitation) and SDG 11 (Sustainable Cities and Communities) amid rapid industrialization and urbanization.
North America
Holding a 27.4% share, the North American market is focused on modernizing aging infrastructure to enhance efficiency, reliability, and resilience. This aligns with SDG 9 by upgrading technological capabilities and ensures the long-term achievement of SDG 6. The increasing adoption of automation supports the principles of SDG 12.
Europe
With a 24.6% share, the European market emphasizes advanced technology, sustainability, and the circular economy. This focus on water reuse, energy efficiency, and nutrient recovery positions the region as a leader in implementing advanced targets within SDG 6 and fully embracing the principles of SDG 12.
Competitive Landscape and Innovation for Sustainable Development
The polymer mixing unit market is moderately fragmented, with competition increasingly centered on factors that promote sustainability. Key differentiators include:
- Automation and Monitoring: Advanced systems that enable precise chemical management contribute to resource efficiency, supporting SDG 12.
- Energy Efficiency: The development of low-energy mixing mechanisms directly supports SDG 7 and reduces the operational carbon footprint of water treatment.
- Reliability and Longevity: Durable equipment ensures the consistent and uninterrupted operation of treatment facilities, which is critical for continuous compliance with environmental standards under SDG 6.
- Modular and Flexible Designs: Innovations in system design that allow for rapid deployment and scalability support the goal of building resilient and adaptable infrastructure under SDG 9.
Strategic imperatives for market leaders involve expanding service networks to support global infrastructure development and investing in technologies that optimize chemical use, reduce energy consumption, and enhance the overall sustainability of water management practices worldwide.
Which SDGs are addressed or connected to the issues highlighted in the article?
-
SDG 6: Clean Water and Sanitation
The article is fundamentally about the technology used for water and wastewater treatment. It directly addresses the global need for clean water and effective sanitation by discussing polymer mixing units, which are essential for “efficient water and wastewater treatment operations,” “sludge dewatering,” and improving “effluent discharge quality.” The text emphasizes drivers like “stricter regulatory mandates” on water quality and “rising awareness of water scarcity issues,” which are central to SDG 6.
-
SDG 9: Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure
This goal is connected through the article’s focus on infrastructure development, technological innovation, and industrial sustainability. The market growth is driven by “municipal infrastructure development and rehabilitation projects” and “aging water treatment infrastructure… requiring equipment replacement and modernization.” Furthermore, the article highlights technological advances such as “automation and digital monitoring,” “energy-efficient mixing mechanisms,” and “smart polymer mixing units,” which align with the goal of upgrading infrastructure and promoting clean technologies in industries like paper, chemical, and power generation.
-
SDG 11: Sustainable Cities and Communities
The article links the demand for polymer mixing units to the challenges of urbanization. It states that “rapid urbanization in emerging markets” and “urban population growth in developing regions” are key drivers necessitating “new wastewater treatment capacity.” By improving municipal wastewater management, this technology contributes to reducing the environmental impact of cities and ensuring access to basic services, which is a core component of sustainable urban development.
-
SDG 12: Responsible Consumption and Production
This goal is addressed through the article’s emphasis on resource efficiency and waste reduction. The technology helps industries and municipalities “reduce chemical waste,” “optimize polymer utilization,” and lower “overall sludge handling costs.” The text also points to a trend towards “sustainable water management,” including “water reuse, zero liquid discharge, and circular economy principles,” all of which are key to achieving sustainable production patterns.
What specific targets under those SDGs can be identified based on the article’s content?
-
SDG 6: Clean Water and Sanitation
- Target 6.1: Achieve universal and equitable access to safe and affordable drinking water for all. The article connects to this target by mentioning that polymer mixing units are used in “potable water production facilities” and are driven by “drinking water quality standards.”
- Target 6.3: Improve water quality by reducing pollution, halving the proportion of untreated wastewater, and substantially increasing recycling and safe reuse. This is the most directly supported target. The article’s entire focus is on equipment for “wastewater treatment,” improving “effluent discharge quality,” and managing “industrial effluent.” It explicitly mentions “growing industrial water recycling initiatives” and “water reuse” as market drivers.
-
SDG 9: Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure
- Target 9.1: Develop quality, reliable, sustainable and resilient infrastructure. The article discusses “Substantial global investments in water and wastewater treatment infrastructure,” the need for “aging facility replacement,” and “new treatment plant construction,” all of which relate to developing and upgrading essential infrastructure.
- Target 9.4: Upgrade infrastructure and retrofit industries to make them sustainable, with increased resource-use efficiency and greater adoption of clean and environmentally sound technologies. The article highlights the adoption of “energy-efficient mixing technologies,” “automated polymer mixing systems,” and “smart water technologies” to enhance sustainability and efficiency in industrial sectors like paper, chemical, and food processing.
-
SDG 11: Sustainable Cities and Communities
- Target 11.6: Reduce the adverse per capita environmental impact of cities, including by paying special attention to… municipal and other waste management. The article directly addresses this by focusing on “municipal wastewater treatment plants” and “biosolids dewatering applications,” which are critical components of managing urban waste and reducing pollution from cities.
-
SDG 12: Responsible Consumption and Production
- Target 12.2: Achieve the sustainable management and efficient use of natural resources. The article points to an “increasing industrial focus on water reuse, zero liquid discharge, and circular economy principles,” which are direct strategies for the sustainable management of water resources.
- Target 12.4: Achieve the environmentally sound management of chemicals and all wastes. The technology discussed aims to “reduce chemical waste” and prevent “polymer overdosing,” contributing to the sound management of chemicals used in water treatment.
- Target 12.5: Substantially reduce waste generation through prevention, reduction, recycling and reuse. The article mentions that these units are crucial for “sludge dewatering,” which reduces the final volume of waste, and supports “water recycling” and “resource recovery” initiatives.
Are there any indicators mentioned or implied in the article that can be used to measure progress towards the identified targets?
-
SDG 6: Clean Water and Sanitation
- Proportion of wastewater safely treated: The growth of the polymer mixing unit market, particularly in the “Wastewater Treatment” application segment which holds a “44.6% market share,” serves as a proxy indicator for the expansion of wastewater treatment capacity globally.
- Investment in water and sanitation infrastructure: The article provides direct financial data that can be used as an indicator, such as the market’s projected growth from “USD 525.2 million in 2025 to approximately USD 659.3 million by 2035.”
-
SDG 9: Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure
- Adoption of advanced and environmentally sound technologies: The article implies this can be measured by the market shift towards “automated mixing systems with integrated monitoring,” “smart water technologies,” and “energy-efficient mixing technologies.” The market share of these advanced systems would be a relevant indicator.
-
SDG 11: Sustainable Cities and Communities
- Proportion of urban population with access to safely managed sanitation services: The article’s discussion of “massive water infrastructure investments across China, India, Southeast Asia” driven by “rapid urbanization” implies that the deployment of these units in new municipal treatment plants is a measure of progress in expanding sanitation services in cities.
-
SDG 12: Responsible Consumption and Production
- Rate of water recycling and reuse: The article identifies “growing industrial water recycling initiatives” and a focus on “zero liquid discharge” as key market drivers. The adoption rate of polymer mixing units in these specific applications can serve as an indicator of progress.
- Reduction in chemical waste: The effectiveness of advanced polymer mixing units, which are designed to “reduce chemical waste” and “minimize waste from over-application,” can be measured to track progress in reducing chemical pollution from industrial and municipal sources.
SDGs, Targets and Indicators
| SDGs | Targets | Indicators |
|---|---|---|
| SDG 6: Clean Water and Sanitation | Target 6.1: Achieve universal and equitable access to safe and affordable drinking water for all. | Investment in and deployment of technology for “potable water production facilities.” |
| Target 6.3: Improve water quality by reducing pollution, halving the proportion of untreated wastewater, and substantially increasing recycling and safe reuse. | Market size and growth for wastewater treatment equipment (from “USD 525.2 million in 2025”); adoption rate of units in “water recycling initiatives.” | |
| SDG 9: Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure | Target 9.1: Develop quality, reliable, sustainable and resilient infrastructure. | Financial investment in water infrastructure, reflected by the market’s “CAGR of 2.3%”; rate of “aging infrastructure replacement.” |
| Target 9.4: Upgrade infrastructure and retrofit industries to make them sustainable, with increased resource-use efficiency and greater adoption of clean and environmentally sound technologies. | Market share of “automated,” “smart,” and “energy-efficient” polymer mixing units. | |
| SDG 11: Sustainable Cities and Communities | Target 11.6: Reduce the adverse per capita environmental impact of cities, including… municipal and other waste management. | Expansion of “municipal wastewater treatment” capacity in urbanizing regions (e.g., Asia Pacific, Latin America). |
| SDG 12: Responsible Consumption and Production | Target 12.2: Achieve the sustainable management and efficient use of natural resources. | Adoption rate of systems supporting “water reuse, zero liquid discharge, and circular economy principles.” |
| Target 12.4: Achieve the environmentally sound management of chemicals and all wastes. | Measured reduction in “chemical waste” and “polymer overdosing” through the use of advanced systems. | |
| Target 12.5: Substantially reduce waste generation through prevention, reduction, recycling and reuse. | Increased efficiency in “sludge dewatering” to reduce waste volume; growth in “water recycling” applications. |
Source: futuremarketinsights.com
What is Your Reaction?
 Like
0
Like
0
 Dislike
0
Dislike
0
 Love
0
Love
0
 Funny
0
Funny
0
 Angry
0
Angry
0
 Sad
0
Sad
0
 Wow
0
Wow
0















































;Resize=620#)






























