Zero Liquid Discharge System Market Size Report, 2033 – Grand View Research
Zero Liquid Discharge Systems Market: A Report on Sustainable Industrial Water Management
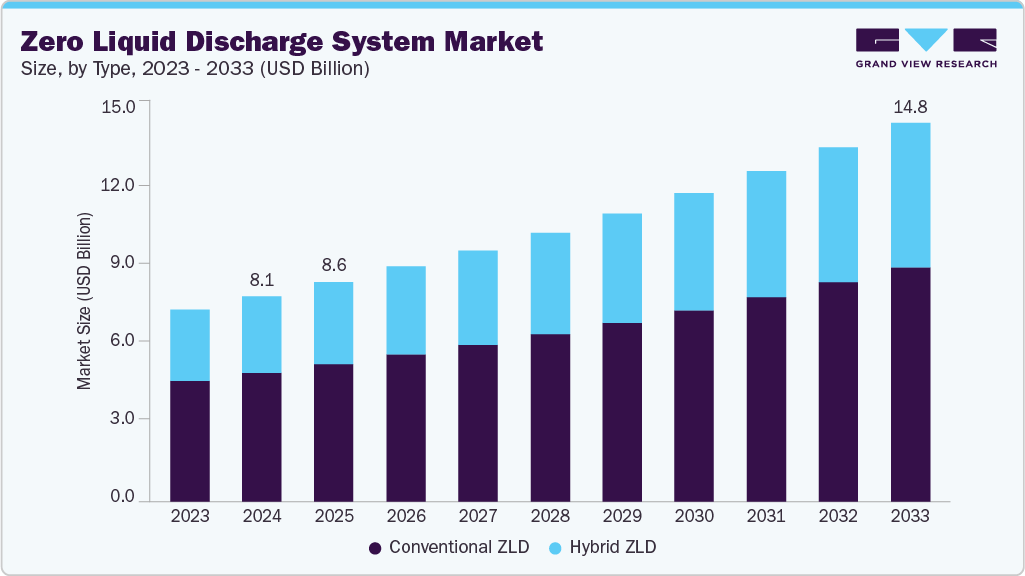
The global market for Zero Liquid Discharge (ZLD) systems is undergoing significant expansion, driven by an urgent global imperative to align industrial practices with the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). The market, valued at USD 8,045.0 million in 2024, is projected to reach USD 14,847.8 million by 2033, reflecting a Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 7.1%. This growth is a direct response to the increasing need for sustainable wastewater management, directly supporting SDG 6 (Clean Water and Sanitation) and SDG 12 (Responsible Consumption and Production).
Market Dynamics and Contribution to Sustainable Development Goals
The ZLD systems market is shaped by a complex interplay of regulatory pressures, technological innovation, and economic factors, all of which are intrinsically linked to achieving global sustainability targets.
Drivers Aligned with SDGs
- Regulatory Frameworks for Environmental Protection: The enforcement of stringent environmental regulations on industrial effluent is a primary market driver. These policies compel industries to adopt ZLD technologies, contributing to the reduction of water pollution and the protection of aquatic ecosystems, a core target of SDG 6.
- Water Scarcity and Resource Management: Growing global awareness of water scarcity necessitates the adoption of circular water management strategies. ZLD systems are critical for achieving SDG 12 by enabling water recycling and reuse, thereby reducing the freshwater footprint of industrial operations.
Opportunities for Sustainable Innovation
- Technological Advancements: Innovations in membrane filtration, evaporation, and crystallization are enhancing the energy efficiency and reducing the operational costs of ZLD systems. This progress supports SDG 9 (Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure) by making sustainable technologies more accessible to a wider range of industries.
- Industrial Growth in Developing Economies: The expansion of industrial sectors in developing nations presents a significant opportunity to integrate sustainable water management from the outset. Implementing ZLD systems supports responsible industrialization and helps these economies meet their commitments under various SDGs.
Restraints and Challenges
- High Capital and Operational Costs: The substantial initial investment and energy-intensive nature of some ZLD processes pose a significant barrier, particularly for small and medium-sized enterprises. Overcoming this challenge is crucial for the equitable achievement of SDG 9 and SDG 12 across all industrial scales.
Segment Analysis in the Context of Sustainable Development
By Type
- Conventional ZLD: This segment, holding a 62.8% market share in 2024, relies on established thermal processes. While effective, its high energy consumption presents challenges to SDG 13 (Climate Action).
- Hybrid ZLD: Projected to grow at a CAGR of 7.4%, this segment combines membrane and thermal technologies. This approach significantly improves energy efficiency, representing a key innovation that aligns with SDG 9 and promotes more sustainable production patterns under SDG 12.
By Technology
- Thermal Based: Dominating the market with a 61.6% share in 2024, thermal-based systems are essential for treating highly complex effluents, ensuring industries can meet zero discharge mandates and protect water resources (SDG 6).
- Membrane Based: This segment is poised for rapid growth, with a projected CAGR of 7.2%. The increasing adoption of membrane technologies like reverse osmosis reduces the overall energy footprint of water treatment, contributing positively to climate action goals (SDG 13).
By End Use
- Power Sector: As the largest end-use segment (32.4% share in 2024), the power industry’s adoption of ZLD is critical for sustainable energy production. It minimizes the sector’s impact on local water sources, aligning with SDG 6 and SDG 7 (Affordable and Clean Energy).
- Metallurgy & Mining: This sector’s growing use of ZLD systems addresses the urgent need to prevent water contamination from mining operations. This directly supports SDG 6 by protecting water quality and SDG 12 by promoting responsible resource extraction.
Regional Analysis and SDG Implementation
Asia Pacific
Dominating the market with a 35.9% revenue share, the Asia Pacific region’s rapid industrialization is coupled with increasing regulatory pressure to manage water resources sustainably. The adoption of ZLD systems is crucial for the region to balance economic growth (SDG 8) with environmental protection (SDG 6, SDG 11).
North America
With a projected CAGR of 7.2%, the North American market is driven by strong regulatory enforcement and a corporate focus on sustainability. The adoption of advanced ZLD technologies supports the region’s commitment to SDG 9 and SDG 12 by fostering clean and resilient industrial infrastructure.
Europe
Europe’s market growth is propelled by stringent EU-wide environmental standards and a commitment to a circular economy. The implementation of ZLD systems is a key strategy for industries to achieve compliance and contribute to the continent’s ambitious sustainability targets, including those under SDG 11 (Sustainable Cities and Communities).
Middle East & Africa
In a region characterized by significant water scarcity, ZLD systems are a vital technology for industrial survival and sustainability. Their adoption is fundamental to achieving water security (SDG 6) and enabling sustainable industrial development.
Latin America
Growing environmental awareness and stricter regulations in sectors like mining and manufacturing are driving ZLD adoption in Latin America. This trend supports the region’s efforts to protect its rich biodiversity and ensure the long-term availability of clean water resources (SDG 6).
Competitive Landscape and Corporate Responsibility
The ZLD market is moderately fragmented, featuring global engineering firms and specialized solution providers. Key players are advancing the sustainability agenda through continuous innovation and strategic acquisitions.
Key Companies Profiled
- Alfa Laval
- GEA Group Aktiengesellschaft
- Aquatech International LLC
- Veolia Water Technologies
- Siemens
- SUEZ Water Technologies & Solutions
- Praj Industries
- Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Ltd.
These companies contribute to the SDGs by developing more energy-efficient systems, expanding access to sustainable water treatment technologies, and enabling industries worldwide to minimize their environmental footprint. Their R&D efforts are central to advancing SDG 9 by creating the innovative infrastructure required for a sustainable future.
Market Projections Summary
- 2024 Market Size: USD 8,045.0 Million
- 2033 Projected Market Size: USD 14,847.8 Million
- Forecast Period CAGR (2025-2033): 7.1%
- Largest Regional Market (2024): Asia Pacific
Analysis of Sustainable Development Goals in the Article
1. Which SDGs are addressed or connected to the issues highlighted in the article?
-
SDG 6: Clean Water and Sanitation
- The article’s central theme is the Zero Liquid Discharge (ZLD) system market, which is directly focused on “sustainable wastewater management” and minimizing “water pollution.” The technology aims to eliminate the discharge of liquid waste from industrial processes, thereby protecting water resources. This aligns perfectly with the goal of ensuring the availability and sustainable management of water and sanitation for all.
-
SDG 9: Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure
- The article discusses how industries like “power generation, chemicals, and pharmaceuticals are increasingly implementing these systems.” This represents a move towards retrofitting industries to make them more sustainable. It also highlights “advancements in membrane filtration, evaporation, and crystallization technologies,” which points to the innovation aspect of this SDG, promoting clean and environmentally sound technologies.
-
SDG 12: Responsible Consumption and Production
- ZLD systems are a key enabler of sustainable production patterns. The article emphasizes that these systems “recover and recycle water while eliminating liquid waste discharge.” This directly supports the goal of achieving the sustainable management and efficient use of natural resources (water) and substantially reducing waste generation through recycling and reuse, as mentioned in the context of “circular water management and sustainability.”
2. What specific targets under those SDGs can be identified based on the article’s content?
-
Under SDG 6: Clean Water and Sanitation
- Target 6.3: By 2030, improve water quality by reducing pollution, eliminating dumping and minimizing release of hazardous chemicals and materials, halving the proportion of untreated wastewater and substantially increasing recycling and safe reuse globally. The article directly addresses this by describing ZLD systems that “eliminate liquid waste,” “reduce environmental impact,” and “recover and recycle water for reuse.”
- Target 6.4: By 2030, substantially increase water-use efficiency across all sectors and ensure sustainable withdrawals and supply of freshwater to address water scarcity. The article highlights that ZLD adoption is driven by “growing awareness of water scarcity” and helps industries reduce “freshwater dependency” through water reuse.
-
Under SDG 9: Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure
- Target 9.4: By 2030, upgrade infrastructure and retrofit industries to make them sustainable, with increased resource-use efficiency and greater adoption of clean and environmentally sound technologies and industrial processes. The article details how various industrial sectors are adopting “advanced, eco-friendly water treatment systems” and how “technological advancements” in ZLD systems are improving efficiency and making them more feasible for a broader range of industries.
-
Under SDG 12: Responsible Consumption and Production
- Target 12.2: By 2030, achieve the sustainable management and efficient use of natural resources. The article’s focus on “water reuse,” “resource recovery,” and “sustainable resource management” directly relates to the efficient use of water as a natural resource.
- Target 12.5: By 2030, substantially reduce waste generation through prevention, reduction, recycling and reuse. The core purpose of a ZLD system is to “eliminate liquid waste discharge,” which is the ultimate form of waste reduction in this context, achieved through comprehensive water recycling and reuse.
3. Are there any indicators mentioned or implied in the article that can be used to measure progress towards the identified targets?
-
Market Size and Growth Rate of ZLD Systems
- The article provides specific financial data, such as the market size being “USD 8,045.0 million in 2024” and a projected “CAGR of 7.1% from 2025 to 2033.” This serves as a powerful proxy indicator for the level of investment and adoption of advanced wastewater treatment technologies by industries globally, directly measuring progress towards Target 6.3 and Target 9.4.
-
Adoption Rate of Advanced and Efficient Technologies
- The article mentions that the “hybrid ZLD segment is expected to grow at a considerable CAGR of 7.4%” and the “membrane based segment is projected to grow rapidly.” These figures act as indicators for the adoption of more energy-efficient and sustainable technologies (Target 9.4) over conventional ones, reflecting a shift towards more sustainable industrial processes.
-
Sector-Specific Market Share and Growth
- The article notes that the “power sector dominated the market with a share of 32.4% in 2024” and is expected to grow significantly. This data can be used as an indicator to track the progress of increasing water-use efficiency (Target 6.4) and sustainable practices within specific high-impact industrial sectors.
4. Table of SDGs, Targets, and Indicators
| SDGs | Targets | Indicators |
|---|---|---|
| SDG 6: Clean Water and Sanitation | Target 6.3: Improve water quality by reducing pollution, eliminating dumping, and substantially increasing recycling and safe reuse globally. | The global market size and growth rate of ZLD systems, which directly reflects the investment in technologies that eliminate liquid waste discharge and promote water recycling (e.g., Market size of USD 8,045.0 million in 2024, growing at a CAGR of 7.1%). |
| Target 6.4: Substantially increase water-use efficiency across all sectors and address water scarcity. | Market share and growth of ZLD systems in key industrial sectors like power generation (32.4% market share), indicating the rate of adoption of water reuse and efficiency technologies to reduce freshwater dependency. | |
| SDG 9: Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure | Target 9.4: Upgrade infrastructure and retrofit industries to make them sustainable, with greater adoption of clean and environmentally sound technologies. | The growth rate of specific advanced and energy-efficient ZLD technologies, such as the projected CAGR of 7.4% for the hybrid ZLD segment, which measures the shift towards cleaner industrial processes. |
| SDG 12: Responsible Consumption and Production | Target 12.2: Achieve the sustainable management and efficient use of natural resources. | The overall market expansion of ZLD systems, which are designed to “recover and recycle water,” indicating an increasing industrial focus on the efficient and sustainable management of water resources. |
| Target 12.5: Substantially reduce waste generation through prevention, reduction, recycling and reuse. | The adoption of ZLD systems, whose primary function is to “eliminate liquid waste discharge,” serves as a direct measure of industry efforts to reduce waste generation through recycling and reuse. |
Source: grandviewresearch.com
What is Your Reaction?
 Like
0
Like
0
 Dislike
0
Dislike
0
 Love
0
Love
0
 Funny
0
Funny
0
 Angry
0
Angry
0
 Sad
0
Sad
0
 Wow
0
Wow
0











































































