Supplement For High Blood Pressure Clears Signs of Alzheimer’s in Mice – ScienceAlert
Report on a Novel Alzheimer’s Treatment and its Alignment with Sustainable Development Goals
Introduction
A recent study by researchers from Kindai University and Japan’s National Institute of Neuroscience has identified a promising new therapeutic avenue for Alzheimer’s disease. The research demonstrates that the amino acid arginine, administered orally, can clear the harmful amyloid-beta protein plaques characteristic of the disease in animal models. This report analyzes these findings with a significant emphasis on their contribution to the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), particularly SDG 3 (Good Health and Well-being).
Key Research Findings
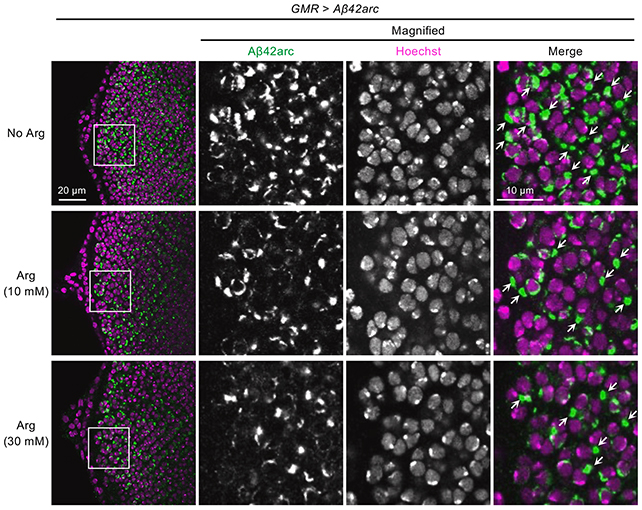
The study focused on the efficacy of arginine in mitigating the molecular symptoms of Alzheimer’s disease. The primary outcomes observed in preclinical models (mice and fruit flies) are as follows:
- Amyloid-Beta Plaque Reduction: Arginine was shown to suppress the aggregation of amyloid-beta proteins both in vitro and in vivo, effectively clearing the sticky protein clumps in the brains of mice and the eyes of fruit flies.
- Reversal of Harm: Beyond plaque removal, the treatment alleviated related toxic effects, reduced behavioral abnormalities in mice, and decreased the activity of neuroinflammatory genes.
- Administration and Safety: The treatment was administered orally via drinking water. Arginine is an existing medication known to be clinically safe and inexpensive, making it a strong candidate for drug repositioning.
Implications for Sustainable Development Goal 3 (Good Health and Well-being)
This research directly supports the achievement of SDG 3, which aims to ensure healthy lives and promote well-being for all at all ages. The potential development of an arginine-based therapy for Alzheimer’s aligns with several key targets:
- Target 3.4: By seeking an effective treatment for Alzheimer’s, a major non-communicable disease (NCD), this work contributes directly to the goal of reducing premature mortality from NCDs and promoting mental health and well-being.
- Accessible Healthcare: The low cost and established safety profile of arginine could lead to a widely accessible treatment, helping to achieve universal health coverage and access to quality essential medicines.
- Healthy Aging: By addressing a disease that predominantly affects older populations, this research promotes healthy aging and well-being, a cornerstone of SDG 3.
Broader SDG Contributions
The implications of this study extend beyond SDG 3, contributing to a wider framework of sustainable development.
- SDG 9 (Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure): The study exemplifies scientific innovation (Target 9.5) by exploring drug repositioning. This is an efficient and sustainable approach to pharmaceutical development that leverages existing resources to address new health challenges.
- SDG 10 (Reduced Inequalities): An affordable and easily administered treatment for Alzheimer’s would significantly reduce health inequalities. It would provide a viable option for low- and middle-income countries and vulnerable populations who may not have access to more expensive therapies.
- SDG 17 (Partnerships for the Goals): The collaboration between a university and a national neuroscience institute highlights the importance of partnerships in advancing scientific research for the global good.
Conclusion and Future Outlook
The findings present arginine as a highly promising, safe, and cost-effective candidate for treating Alzheimer’s disease. While the results from animal models are encouraging, further research is required to determine safe and effective dosages for humans, and clinical trials are the necessary next step. The uncertainty regarding the primary role of amyloid-beta plaques in Alzheimer’s progression remains a consideration. Nevertheless, this research represents a significant step forward, opening new possibilities for developing therapies for neurodegenerative diseases and advancing the global commitment to health, innovation, and equality as defined by the Sustainable Development Goals.
Analysis of Sustainable Development Goals in the Article
-
Which SDGs are addressed or connected to the issues highlighted in the article?
The article primarily addresses issues related to the following Sustainable Development Goals:
- SDG 3: Good Health and Well-being: The core focus of the article is on Alzheimer’s disease, a major health concern, and the scientific discovery of a potential new treatment. The research aims to improve the health outcomes for individuals suffering from this neurodegenerative disease.
- SDG 9: Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure: The article highlights scientific research and innovation as a means to address a significant health challenge. It discusses the work of researchers from “Kindai University and Japan’s National Institute of Neuroscience,” which falls under the umbrella of enhancing scientific research and technological capabilities.
-
What specific targets under those SDGs can be identified based on the article’s content?
Based on the article’s content, the following specific targets can be identified:
- Target 3.4: By 2030, reduce by one-third premature mortality from non-communicable diseases through prevention and treatment and promote mental health and well-being. The research on a new treatment for Alzheimer’s, a non-communicable disease, directly contributes to this target. The article states the goal is “tackling a key molecular symptom of Alzheimer’s” which is a step towards effective treatment.
- Target 3.b: Support the research and development of vaccines and medicines for the communicable and non-communicable diseases. The article is entirely focused on the research and potential development of a new therapeutic option for Alzheimer’s. The text mentions that the findings “open up new possibilities for developing arginine-based strategies for neurodegenerative diseases.”
- Target 9.5: Enhance scientific research, upgrade the technological capabilities of industrial sectors in all countries… encouraging innovation. The article is a report on a scientific study published in Neurochemistry International. It describes the innovative approach of using arginine to “suppress amyloid-beta aggregation” and highlights the research conducted by Japanese institutions, which is a direct example of enhancing scientific research.
-
Are there any indicators mentioned or implied in the article that can be used to measure progress towards the identified targets?
While the article does not mention official SDG indicators, it implies several metrics that can be used to measure progress:
- For Target 3.4: Progress can be measured by the effectiveness of the treatment in animal models. The article implies indicators such as the “reduction of protein build-up in the animals’ brains,” alleviation of “toxic effects,” and reduced “behavioral abnormalities.” These are measurable outcomes of the experimental treatment.
- For Target 3.b: An implied indicator is the development of accessible and affordable treatments. The article emphasizes that arginine is “already known to be clinically safe and inexpensive,” making it a “highly promising candidate” for a new therapy. The progression of this research into “clinical trials” would be a key indicator of progress.
- For Target 9.5: The publication of the research itself is an indicator of scientific output. The article mentions the study was published in “Neurochemistry International,” which serves as a formal indicator of completed and peer-reviewed scientific research, contributing to the global knowledge base on Alzheimer’s treatment.
-
Create a table with three columns titled ‘SDGs, Targets and Indicators” to present the findings from analyzing the article.
SDGs Targets Indicators (Implied from the article) SDG 3: Good Health and Well-being Target 3.4: Reduce premature mortality from non-communicable diseases through prevention and treatment. Reduction of amyloid-beta plaques and alleviation of related toxic effects and behavioral abnormalities in animal models. SDG 3: Good Health and Well-being Target 3.b: Support the research and development of medicines for non-communicable diseases. Development of new, safe, and inexpensive therapeutic options (like arginine) and their progression to clinical trials. SDG 9: Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure Target 9.5: Enhance scientific research and encourage innovation. Publication of scientific research in peer-reviewed journals (e.g., Neurochemistry International).
Source: sciencealert.com
What is Your Reaction?
 Like
0
Like
0
 Dislike
0
Dislike
0
 Love
0
Love
0
 Funny
0
Funny
0
 Angry
0
Angry
0
 Sad
0
Sad
0
 Wow
0
Wow
0












































































