Harnessing the Sun for Sustainable Water: Solar Water Desalination Plant Market to Reach US$ 5.1 Bn by 2035 – openPR.com
Solar Water Desalination Market: A Report on Sustainable Water Solutions
Market Overview and Projections
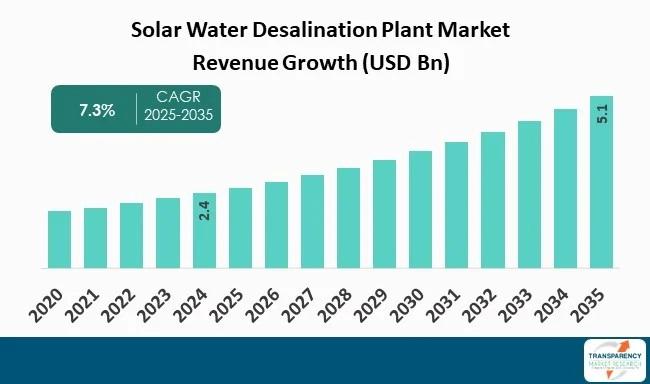
The global solar water desalination plant market is experiencing significant growth, driven by the increasing global imperatives of freshwater security, rising energy costs, and climate change mitigation. The market was valued at US$ 2.4 billion in 2024 and is projected to expand at a Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 7.3% from 2025 to 2035, reaching an estimated US$ 5.1 billion. This expansion reflects a global shift towards sustainable technologies that directly support the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) by harnessing solar energy to produce potable water from saline sources.
Alignment with Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs)
Solar water desalination technology is a critical tool for achieving several key SDGs by providing a sustainable and environmentally responsible solution to water scarcity.
SDG 6: Clean Water and Sanitation
With over 40% of the global population affected by water scarcity, solar desalination directly addresses the core targets of SDG 6. It provides a viable method for increasing the availability of clean drinking water, particularly in arid, remote, and coastal regions, thereby enhancing water security for communities and industries.
SDG 7: Affordable and Clean Energy
By utilizing solar power, these desalination plants reduce dependence on fossil fuels, which power traditional energy-intensive desalination methods. This aligns with SDG 7 by promoting the use of clean, renewable energy, reducing long-term operational costs, and enabling water production in off-grid locations.
SDG 13: Climate Action
The transition from fossil fuel-based desalination to solar-powered systems contributes significantly to SDG 13. It lowers greenhouse gas emissions, helping nations meet their commitments under international climate frameworks such as the Paris Agreement and taking urgent action to combat climate change.
SDG 9: Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure
The market’s growth is fueled by continuous innovation in solar and desalination technologies. The development of hybrid systems, advanced membranes, and smart monitoring solutions fosters innovation and builds resilient, sustainable water infrastructure, a key component of SDG 9.
Key Market Growth Drivers
-
Addressing Global Water Scarcity (SDG 6)
The primary driver is the escalating demand for potable water due to population growth, urbanization, and the depletion of freshwater reserves. Governments in water-stressed regions, including the Middle East, North Africa, and South Asia, are investing in solar desalination to sustainably meet municipal, industrial, and agricultural water needs.
-
Transition to Renewable Energy (SDG 7 & SDG 13)
A strategic global shift towards carbon neutrality is accelerating the integration of renewable energy in water production. The declining cost of solar photovoltaic (PV) systems makes large-scale solar desalination projects more economically feasible and environmentally sound, reducing the carbon footprint of water infrastructure.
-
Technological Innovation (SDG 9)
Advancements are enhancing the efficiency and scalability of solar desalination. Innovations include hybrid systems combining solar thermal and PV, concentrated solar power (CSP), and nanomaterial-based membranes that improve water yield while minimizing energy consumption.
-
Supportive Governance and Investment (SDG 17)
Public-private partnerships, government subsidies, and international funding are crucial for market expansion. These collaborations, aligned with SDG 17, facilitate the development of large-scale projects and promote the adoption of renewable desalination technologies in developing nations.
Emerging Market Trends
-
Hybrid and Decentralized Systems
Hybrid systems integrating solar with other renewables like wind ensure continuous operation, enhancing reliability. Concurrently, decentralized and modular solar units are being deployed in rural and remote communities, providing scalable and cost-effective solutions that support SDG 6 and SDG 11 (Sustainable Cities and Communities).
-
Integration of Smart Technologies
The use of automation, remote monitoring, and data analytics is optimizing plant performance. Smart technologies enable predictive maintenance and improve energy efficiency, contributing to the innovative infrastructure goals of SDG 9.
-
Advancements in Materials Science
Research into advanced materials, such as graphene-based and nanoporous membranes, promises to increase desalination efficiency. These materials resist fouling and scaling, enhancing the performance of reverse osmosis systems and lowering energy requirements.
Regional Analysis and SDG Implementation
Middle East & Africa
This region leads the market, leveraging high solar irradiance and strong government support to combat severe water scarcity. Projects like Saudi Arabia’s Neom are integrating renewable desalination to achieve carbon-neutral water production, directly advancing SDG 6 and SDG 7.
Asia Pacific
The market is expected to grow rapidly due to increasing water stress in countries like India, China, and Australia. Government policies promoting renewable energy are fostering the adoption of solar desalination to support agriculture and rural water supply schemes.
Europe
Nations such as Spain and Greece are adopting solar desalination to improve water security in drought-prone Mediterranean regions. The EU’s focus on a green energy transition supports research and development in this field.
North America
A growing market, particularly in the southwestern U.S. and Mexico, where water scarcity is a major concern. Pilot projects are exploring the integration of solar power with advanced desalination for sustainable water management.
Latin America
Countries like Chile and Peru are utilizing their extensive coastlines and high solar potential to provide potable water for mining operations and coastal communities, demonstrating a practical application of technology to meet SDG 6.
Competitive Landscape
The market is moderately fragmented, with key players focusing on innovation, strategic partnerships, and project expansion to advance sustainable water solutions.
Key Industry Players
- Acciona S.A.
- ACWA Power
- Caterpillar Inc.
- Elemental Water Makers B.V.
- F Cubed Limited
- Photon Energy Systems Limited
- Sinovoltaics Group
- Solar Water Solutions Ltd.
- Sterlitech Corporation
- Tesla, Inc.
- Trunz Water Systems AG
- Veolia Environnement SA
- Waaree Energies Ltd
These companies are investing in hybrid technologies and AI-based performance monitoring to expand their market footprint and contribute to global sustainability targets.
Future Outlook
The future of the solar water desalination plant market is highly positive, underpinned by the global imperatives for water security (SDG 6) and a clean energy transition (SDG 7). Continued advancements in technology are expected to make solar desalination more cost-competitive and scalable. As water scarcity intensifies, solar desalination is positioned to become a cornerstone of global water infrastructure, ensuring a secure, renewable, and environmentally friendly water supply for future generations.
Analysis of Sustainable Development Goals in the Article
1. Which SDGs are addressed or connected to the issues highlighted in the article?
-
SDG 6: Clean Water and Sanitation
- The core issue of the article is addressing global water scarcity through solar desalination. It directly mentions that “Water scarcity affects more than 40% of the global population” and that solar desalination provides “fresh, drinkable water from saline sources,” which is central to SDG 6.
-
SDG 7: Affordable and Clean Energy
- The article focuses on using “abundant solar energy” as a power source for desalination, contrasting it with traditional methods that “relying heavily on fossil fuels.” This shift towards a renewable energy source is a key component of SDG 7.
-
SDG 9: Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure
- The text highlights “Technological Advancements and Innovation” such as hybrid systems, advanced membranes, and smart technologies. The development and deployment of solar water desalination plants represent an investment in sustainable and resilient infrastructure, which aligns with SDG 9.
-
SDG 12: Responsible Consumption and Production
- By promoting a technology that reduces dependency on fossil fuels and uses a renewable resource (solar energy) to produce a vital resource (water), the article advocates for more sustainable production patterns. This addresses the goal of achieving sustainable management and efficient use of natural resources.
-
SDG 13: Climate Action
- The article explicitly states that solar desalination helps “reduce greenhouse gas emissions” and supports nations in committing to “carbon neutrality goals under global frameworks such as the Paris Agreement.” This directly contributes to combating climate change and its impacts.
-
SDG 17: Partnerships for the Goals
- The article mentions that “Public-private partnerships, subsidies, and research grants are playing a critical role” and highlights “International funding from development agencies and climate finance programs.” This emphasizes the importance of collaboration to achieve sustainable development, a core principle of SDG 17.
2. What specific targets under those SDGs can be identified based on the article’s content?
-
Under SDG 6 (Clean Water and Sanitation):
- Target 6.1: By 2030, achieve universal and equitable access to safe and affordable drinking water for all. The article supports this by discussing technology that produces “fresh, drinkable water” for municipal needs, especially in “arid regions where… freshwater is scarce.”
- Target 6.4: By 2030, substantially increase water-use efficiency across all sectors and ensure sustainable withdrawals and supply of freshwater to address water scarcity. The article’s focus on creating a new, sustainable source of freshwater directly addresses the challenge of water scarcity mentioned as affecting “more than 40% of the global population.”
-
Under SDG 7 (Affordable and Clean Energy):
- Target 7.2: By 2030, increase substantially the share of renewable energy in the global energy mix. The entire premise of the article is the growth of the “solar water desalination plant market,” which directly increases the use of solar power, a key renewable energy source.
- Target 7.a: By 2030, enhance international cooperation to facilitate access to clean energy research and technology. The article points to “International funding” and the global adoption of these technologies in regions like the Middle East, Asia Pacific, and Latin America as evidence of this cooperation.
-
Under SDG 9 (Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure):
- Target 9.4: By 2030, upgrade infrastructure and retrofit industries to make them sustainable, with increased resource-use efficiency and greater adoption of clean and environmentally sound technologies. Solar desalination is presented as a “cleaner, more resilient approach to water production” and a sustainable upgrade to traditional, energy-intensive desalination methods.
- Target 9.5: Enhance scientific research, upgrade the technological capabilities of industrial sectors in all countries. The article details “Continuous innovation in both solar and desalination technologies,” including “nanomaterial-based membranes” and “smart sensors,” which reflects an enhancement of technological capabilities.
-
Under SDG 12 (Responsible Consumption and Production):
- Target 12.2: By 2030, achieve the sustainable management and efficient use of natural resources. The technology discussed uses an abundant natural resource (sunlight) to address the scarcity of another (freshwater), reducing reliance on finite resources like fossil fuels and easing the strain on depleted freshwater reserves.
-
Under SDG 13 (Climate Action):
- Target 13.2: Integrate climate change measures into national policies, strategies and planning. The article notes that governments are “actively investing in solar-powered desalination” as nations “commit to carbon neutrality goals,” showing the integration of climate-friendly technology into national water and energy strategies.
-
Under SDG 17 (Partnerships for the Goals):
- Target 17.17: Encourage and promote effective public, public-private and civil society partnerships. The article explicitly cites “Public-private partnerships” and collaborations “between renewable energy providers and water treatment companies” as key drivers for the market.
3. Are there any indicators mentioned or implied in the article that can be used to measure progress towards the identified targets?
-
For SDG 6:
- An implied indicator is the proportion of the population with access to safely managed drinking water services (related to Indicator 6.1.1). The article’s goal of providing “potable water to… coastal populations” and supporting “rural water supply schemes” implies a focus on increasing this proportion.
- The article directly mentions that “Water scarcity affects more than 40% of the global population,” which relates to Indicator 6.4.2: Level of water stress: freshwater withdrawal as a proportion of available freshwater resources. The deployment of desalination plants aims to reduce this stress.
-
For SDG 7:
- The growth of the solar desalination market, “projected to grow at a CAGR of 7.3%… reaching an estimated US$ 5.1 billion by 2035,” serves as a proxy indicator for the increase in the share of renewable energy (Indicator 7.2.1) within the specific sector of water production.
-
For SDG 9:
- Government and private investments in “pilot and commercial-scale projects” in countries like Saudi Arabia, the UAE, and India can be seen as a measure of investment in sustainable infrastructure (related to Indicator 9.a.1).
-
For SDG 13:
- The stated benefit of solar desalination to “reduce greenhouse gas emissions” is a direct reference to the ultimate goal measured by indicators of total greenhouse gas emissions (related to SDG 13 indicators). While the article does not provide specific figures, it identifies the technology as a tool for achieving emission reduction targets.
-
For SDG 17:
- The mention of “Public-private partnerships,” “international funding,” and “collaborations between renewable energy providers and water treatment companies” serves as a qualitative indicator of the value of partnerships for sustainable development (related to Indicator 17.17.1).
4. Summary Table of SDGs, Targets, and Indicators
| SDGs | Targets | Indicators (Mentioned or Implied in the Article) |
|---|---|---|
| SDG 6: Clean Water and Sanitation | 6.1: Achieve universal access to safe and affordable drinking water. 6.4: Increase water-use efficiency and address water scarcity. |
Implied: Increase in the population with access to safely managed drinking water. Mentioned: The fact that “Water scarcity affects more than 40% of the global population” (related to Indicator 6.4.2: Level of water stress). |
| SDG 7: Affordable and Clean Energy | 7.2: Increase the share of renewable energy in the global energy mix. 7.a: Enhance international cooperation for access to clean energy technology. |
Implied: The projected market growth (CAGR of 7.3%) of solar desalination plants as a measure of increased renewable energy share (related to Indicator 7.2.1). |
| SDG 9: Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure | 9.4: Upgrade infrastructure and industries for sustainability. 9.5: Enhance scientific research and upgrade technological capabilities. |
Implied: Government and private investments in large-scale solar desalination projects as a measure of sustainable infrastructure investment (related to Indicator 9.a.1). |
| SDG 12: Responsible Consumption and Production | 12.2: Achieve sustainable management and efficient use of natural resources. | Implied: The shift from fossil-fuel-intensive desalination to renewable-powered systems as an indicator of improved natural resource management. |
| SDG 13: Climate Action | 13.2: Integrate climate change measures into national policies and planning. | Mentioned: The technology’s ability to “reduce greenhouse gas emissions” and help nations meet “carbon neutrality goals.” |
| SDG 17: Partnerships for the Goals | 17.17: Encourage and promote effective public, public-private and civil society partnerships. | Mentioned: The role of “Public-private partnerships,” “international funding,” and “collaborations” as drivers of market growth (related to Indicator 17.17.1). |
Source: openpr.com
What is Your Reaction?
 Like
0
Like
0
 Dislike
0
Dislike
0
 Love
0
Love
0
 Funny
0
Funny
0
 Angry
0
Angry
0
 Sad
0
Sad
0
 Wow
0
Wow
0













































































