Will Technology Save Us? It Might Have To – Legal Planet
Report on Advances in Energy Storage Technology and its Impact on Sustainable Development Goals
Executive Summary
This report analyzes recent developments in electricity battery storage technology, primarily focusing on California as a case study. It assesses the role of these innovations in advancing the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), with a particular emphasis on SDG 7 (Affordable and Clean Energy), SDG 9 (Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure), and SDG 13 (Climate Action). The analysis indicates that rapid growth in battery storage capacity is significantly enhancing the viability of renewable energy sources, thereby contributing to grid stability and the decarbonization of the energy sector.
Technological Advancement and its Contribution to SDG 7: Affordable and Clean Energy
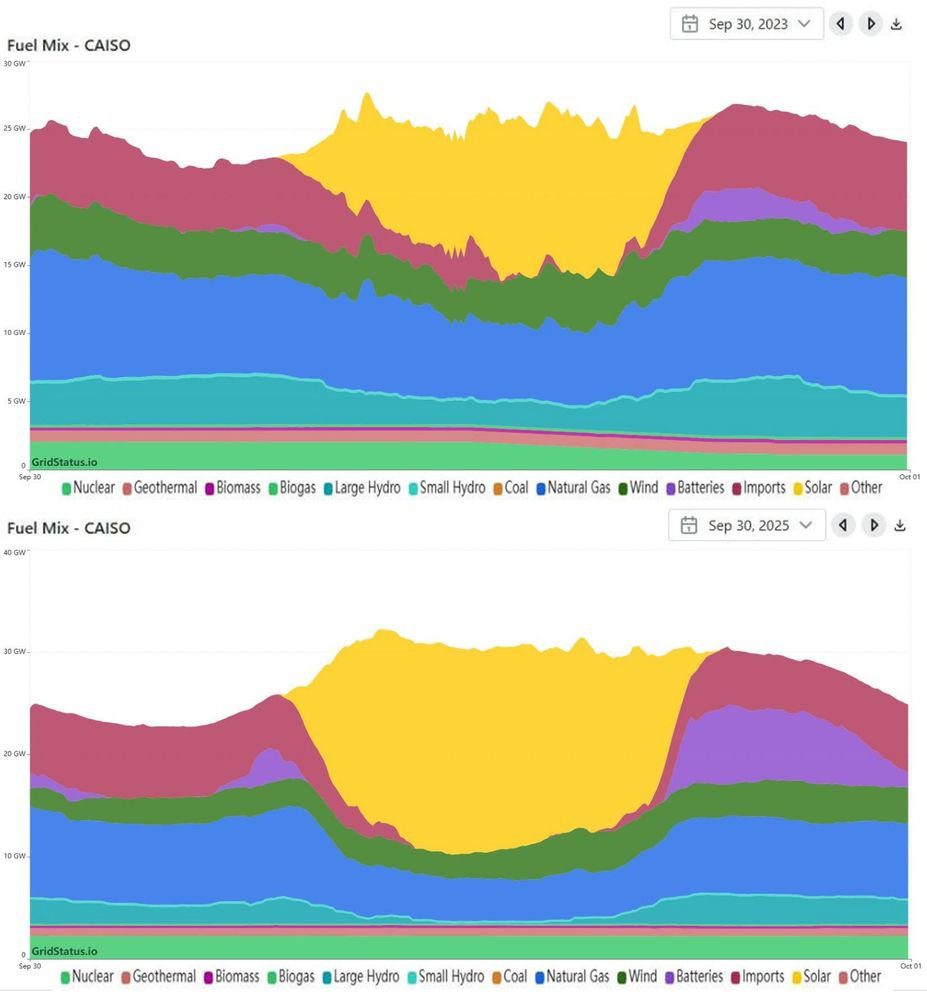
Case Study: California’s Energy Grid Transformation
Data from the California Independent System Operator reveals a significant transformation in the state’s energy profile, directly supporting the objectives of SDG 7.
- Increased Solar Generation: A substantial increase in solar power generation has been observed, particularly during daytime hours.
- Exponential Growth in Battery Storage: The most critical development is the exponential growth in battery storage capacity. This allows for the capture of excess solar energy generated during the day.
- Enhanced Energy Availability: Stored energy is discharged during evening peak demand hours, effectively extending the availability of clean solar power and reducing reliance on other energy sources. According to the Financial Times, California’s battery storage capacity has tripled to 13GW, with further expansion planned.
Impact on Energy Reliability and Accessibility
The deployment of large-scale battery storage systems is crucial for building a resilient and sustainable energy infrastructure.
- Grid Stabilization: By banking solar power for later use, mega-batteries shore up the grid, mitigating the risk of blackouts that have historically challenged the state.
- Maximizing Renewable Energy Use: This technology addresses the intermittency of solar power, a key barrier to its widespread adoption, thus increasing the share of renewables in the energy mix.
- Reducing Fossil Fuel Dependence: The ability to store and discharge clean energy reduces the need for fossil fuel-powered “peaker” plants, which are typically activated during high-demand periods. This directly contributes to the SDG 7 target of increasing the share of renewable energy.
Fostering Climate Action (SDG 13) and Sustainable Innovation (SDG 9)
Decarbonization of the Energy Sector
The expansion of battery storage is a cornerstone of efforts to combat climate change, in line with SDG 13.
- Enabling Decarbonization: Advanced battery technology is a key enabler for decarbonizing the power grid by facilitating a higher penetration of renewable energy sources.
- Widespread Adoption: This trend is not limited to California; states like Texas are also making significant investments in giant battery installations, indicating a broader market shift.
- Global Innovation Leadership: The Financial Times notes that battery technology is central to China’s green energy transition. This global focus ensures continued technological development and innovation, which aligns with the aims of SDG 9 to build resilient infrastructure and foster innovation.
Policy and Geopolitical Context
While technological progress is promising, the policy environment remains a critical factor. Political decisions can significantly impact the pace of renewable energy adoption. However, the global momentum in green technology, driven by nations like China, suggests that innovation will persist. This international dynamic underscores the importance of global cooperation and competition in driving the technological advancements needed to meet the SDGs.
Challenges and Future Outlook
Identified Obstacles to SDG Attainment
Despite positive technological trends, several challenges could impede progress toward clean energy goals.
- Policy Uncertainty: Potential reductions in federal energy credits and policies unsupportive of renewable energy could slow market growth in the United States.
- Rising Energy Demand: The massive growth in energy consumption from data centers and other industrial uses presents a significant challenge to decarbonizing the grid.
Conclusion: Innovation as a Key Driver for Sustainable Development
The rapid development and deployment of battery storage technology offer a source of optimism for achieving global energy and climate goals. Historical precedent, such as the development of the catalytic converter to address air pollution, demonstrates that targeted technological innovation, supported by smart policy, can solve pressing environmental challenges. While obstacles remain, the progress in energy storage indicates that technology is a vital tool in the effort to achieve a sustainable future as outlined by the SDGs.
Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) Addressed
The article addresses or connects to the following SDGs:
-
SDG 7: Affordable and Clean Energy
The core theme of the article is the advancement and implementation of clean energy solutions. It discusses the significant increase in solar generation in California and the crucial role of battery storage technology in making this renewable energy source more reliable and accessible, particularly during peak evening hours. This directly aligns with the goal of ensuring access to affordable, reliable, and sustainable energy.
-
SDG 9: Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure
The article highlights technological innovation as a key driver for the energy transition. The development of “mega batteries” and the rapid expansion of energy storage capacity represent a significant upgrade to energy infrastructure. This focus on new technology and building resilient infrastructure to support clean energy is central to SDG 9.
-
SDG 13: Climate Action
The article explicitly links the adoption of solar power and battery storage to climate action goals. It mentions the objective of “decarbonizing the grid” and reducing “reliance on fossil fuels.” These efforts are direct measures to combat climate change and its impacts, which is the primary focus of SDG 13.
Specific SDG Targets Identified
Based on the article’s content, the following specific targets can be identified:
-
Target 7.2: By 2030, increase substantially the share of renewable energy in the global energy mix.
The article provides direct evidence of progress towards this target in California. It describes a “significant increase in solar generation” between 2023 and 2025 and how battery storage has “extended the state’s use of renewable energy.” The graphic mentioned shows the growing share of solar power in the daily energy mix.
-
Target 9.4: By 2030, upgrade infrastructure and retrofit industries to make them sustainable, with increased resource-use efficiency and greater adoption of clean and environmentally sound technologies and industrial processes.
The “boom in mega battery development” in California is a clear example of upgrading energy infrastructure with clean technology. The article states that these battery installations shore up the grid by banking solar energy during the day and discharging it in the evening, making the entire system more sustainable and efficient.
-
Target 7.a: By 2030, enhance international cooperation to facilitate access to clean energy research and technology… and promote investment in energy infrastructure and clean energy technology.
The article touches on the global nature of clean energy technology development. It notes that “China will take the lead on technological development” in batteries, highlighting the international dimension of research and innovation in this field, which is relevant to this target.
Indicators for Measuring Progress
The article mentions or implies the following indicators to measure progress:
-
Indicator for Target 7.2 (Renewable energy share):
The article provides specific quantitative data that can be used as an indicator. It states that California’s battery storage capacity, which supports the renewable grid, has “more than tripled to 13GW of power, with plans to add another 8.6GW by 2027.” The graphic of daily energy usage also serves as a visual indicator of the proportion of energy generated from solar sources.
-
Indicator for Target 9.4 (Adoption of clean technologies):
The installed capacity of battery storage is a direct indicator of the adoption of this clean technology. The figures of “13GW of power” already installed and the plan for an “another 8.6GW” are concrete metrics that measure the upgrading of infrastructure as described in this target.
-
Indicator for Policy Integration (Relevant to SDG 13):
While not a formal UN indicator, the article implies the importance of policy as a measure of progress. It mentions that the battery boom was “Enabled by state policies” in California. The historical reference to the “Clean Air Act” further supports the idea that the existence and effectiveness of such policies are crucial indicators of a government’s commitment to integrating climate action.
Summary of Findings
| SDGs | Targets | Indicators |
|---|---|---|
| SDG 7: Affordable and Clean Energy | 7.2: Increase substantially the share of renewable energy in the global energy mix. | The share of solar power in California’s daily energy mix, as shown in the graphic. |
| SDG 9: Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure | 9.4: Upgrade infrastructure… with greater adoption of clean and environmentally sound technologies. | Installed battery storage capacity, which has grown to 13GW with plans for an additional 8.6GW. |
| SDG 13: Climate Action | 13.2: Integrate climate change measures into national policies, strategies and planning. | The existence of “state policies” in California that have enabled the boom in mega battery development. |
Source: legal-planet.org
What is Your Reaction?
 Like
0
Like
0
 Dislike
0
Dislike
0
 Love
0
Love
0
 Funny
0
Funny
0
 Angry
0
Angry
0
 Sad
0
Sad
0
 Wow
0
Wow
0













































































